【LetMeFly】1206.设计跳表:算法详解
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-skiplist/
不使用任何库函数,设计一个 跳表 。
跳表 是在 O(log(n)) 时间内完成增加、删除、搜索操作的数据结构。跳表相比于树堆与红黑树,其功能与性能相当,并且跳表的代码长度相较下更短,其设计思想与链表相似。
例如,一个跳表包含 [30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 90] ,然后增加 80、45 到跳表中,以下图的方式操作:
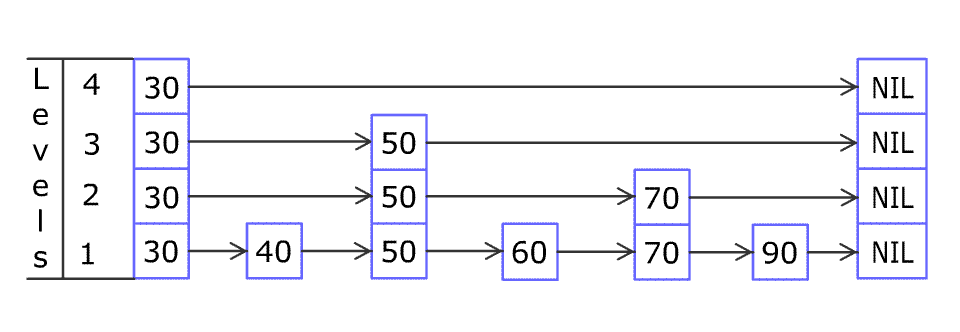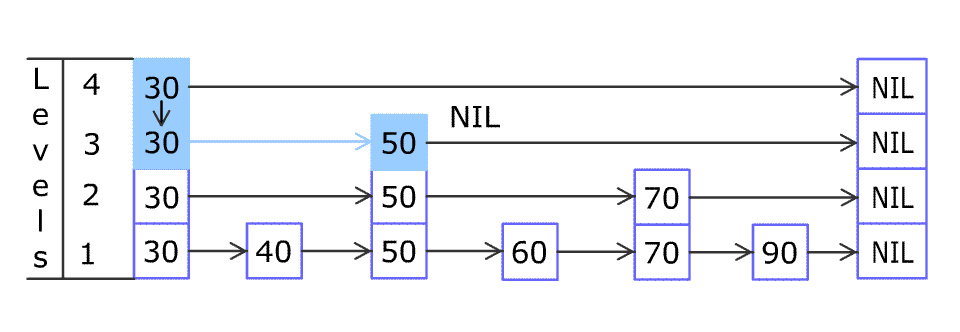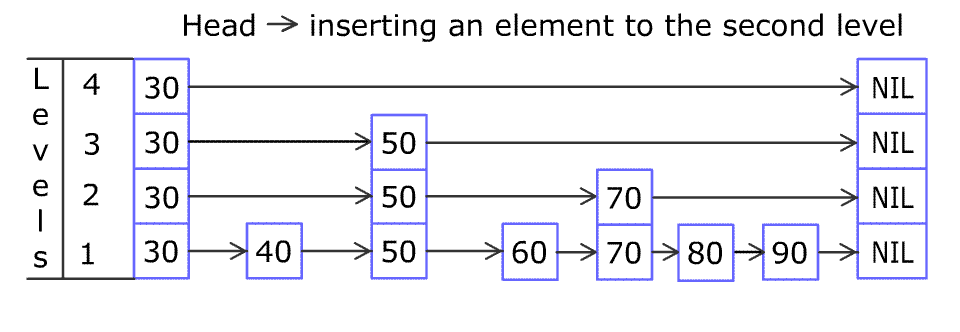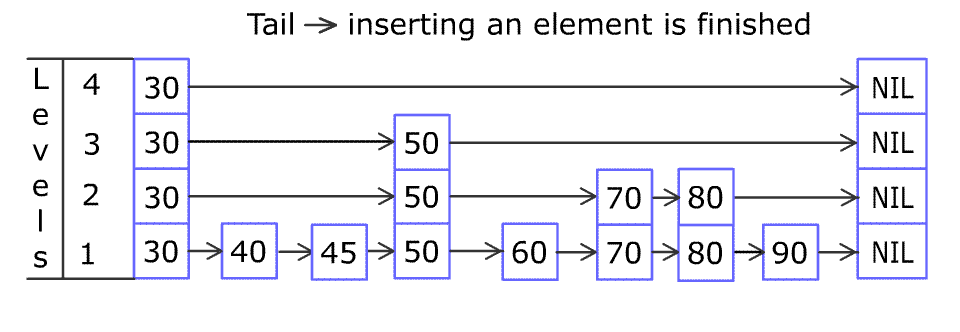
跳表中有很多层,每一层是一个短的链表。在第一层的作用下,增加、删除和搜索操作的时间复杂度不超过 O(n)。跳表的每一个操作的平均时间复杂度是 O(log(n)),空间复杂度是 O(n)。
了解更多 : https://oi-wiki.org/ds/skiplist/
在本题中,你的设计应该要包含这些函数:
bool search(int target): 返回target是否存在于跳表中。void add(int num): 插入一个元素到跳表。bool erase(int num): 在跳表中删除一个值,如果num不存在,直接返回false. 如果存在多个num,删除其中任意一个即可。
注意,跳表中可能存在多个相同的值,你的代码需要处理这种情况。
示例 1:
输入 ["Skiplist", "add", "add", "add", "search", "add", "search", "erase", "erase", "search"] [[], [1], [2], [3], [0], [4], [1], [0], [1], [1]] 输出 [null, null, null, null, false, null, true, false, true, false]解释 Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist(); skiplist.add(1); skiplist.add(2); skiplist.add(3); skiplist.search(0); // 返回 false skiplist.add(4); skiplist.search(1); // 返回 true skiplist.erase(0); // 返回 false,0 不在跳表中 skiplist.erase(1); // 返回 true skiplist.search(1); // 返回 false,1 已被擦除
提示:
0 <= num, target <= 2 * 104- 调用
search,add,erase操作次数不大于5 * 104
设计跳表
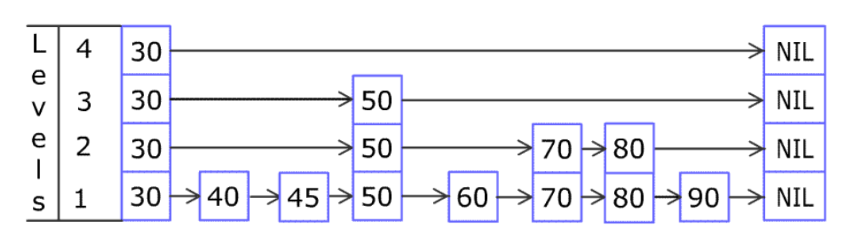
链表查询复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),因为要从头到尾遍历。怎么解决这个问题?多几层链表(最下层level1是全链表),上层链表元素少,先查上层(查一次就能跳过level1好多元素),再查下层,最终查到level1。
节点设计
对于一个节点(例如 50 50 50),我们可以只创建一个 50 50 50节点,并分别保留这个节点在level1到level3的下一个节点。
class SkiplistNode {
public:int value;vector<SkiplistNode*> next;SkiplistNode(int val, int level): value(val), next(level) {} // 一个节点一旦生成,level就是固定的
};
class Skiplist {
private:SkiplistNode* head; // 为了方便,统一添加头节点int level; // 当前跳表层数,可依据实际数据范围确定
public:Skiplist() {head = new SkiplistNode(-1, MAX_LEVEL); // 每层一旦出现,就一定需要head节点level = 0;}bool search(int target) {}void add(int num) {}bool erase(int num) {}
};
查询
- 每一层的查询依据是:找到最后一个严格小于 t a r g e t target target的节点;
- 上层到下层的依据是:同一个节点直接下移一层。
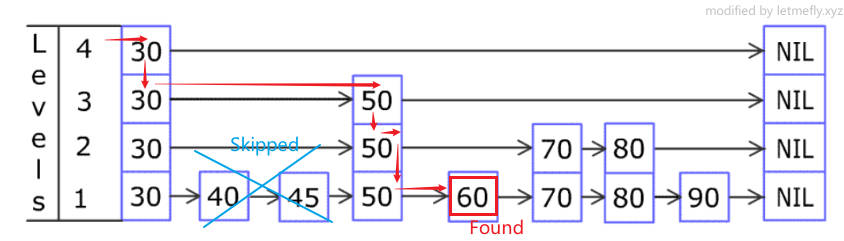
例如上图要查询元素 60 60 60:
- 先从最上层(level4)开始查询, 30 30 30是最后一个小于 60 60 60的元素,在 30 30 30停止,跳到level3的 30 30 30
- level3从 30 30 30开始向右查询, 50 50 50是最后一个小于 60 60 60的元素,直接跳到 50 50 50(可以发现最下层的 40 40 40和 45 45 45d都被跳过了),跳到level2的 50 50 50
- level2从 50 50 50开始向右查询,最后一个小于 60 60 60的节点就是 50 50 50,停止并跳到level1的 50 50 50
- level1从 50 50 50开始向右查询,最后一个小于 60 60 60的节点就是 50 50 50,停止。
最终停止的节点是level1的 50 50 50。
注意:
- 最终一定停止在level1
- 每一层都是在最后一个严格小于target的节点停止并移动到下层(如有)
- 所查询节点就是最终停止到的节点的右边相邻节点
bool search(int target) {SkiplistNode* p = head; // 从头节点开始for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 从上层到下层while (p->next[i] && p->next[i]->value < target) { // 每一层找到最后一个严格小于target的节点p = p->next[i];}}p = p->next[0]; // 最终停止到了level1的50,50在level1的next就是待查找的60return p && p->value == target;
}
插入
新增一个节点,这个节点都要在哪些层出现呢?直接rand呗。每个节点都要在最下层出现,可以定义一个全局概率 P P P,表示这个节点有 P P P的概率在上一层再出现一次。
对于本题,要求复杂度 log 2 n \log_2 n log2n所以可取 P = 1 2 P=\frac12 P=21;最多50000次操作, log 2 50000 ≈ 15.6 \log_2 50000\approx 15.6 log250000≈15.6,因此可取最大层数 15 15 15。
int randLevel() {int ans = 1;while (ans < MAX_LEVEL && rand() < p) {ans++;}return ans;
}
对于新增节点 n u m num num,假设随机出来确定它要在 l e v e l 1 level_1 level1到 l e v e l n e w L e v e l level_{newLevel} levelnewLevel层出现,那么就可以创建一个大小为 n e w L e v e l newLevel newLevel的 u p d a t e update update数组,其中 u p d a t e [ i ] = p update[i]=p update[i]=p代表 l e v e l i + 1 level_{i+1} leveli+1层 p p p元素的 n e x t next next需要修改为指向新节点。
确定 u p d a t e update update数组的方法和查询类似,每层找到最后一个严格小于 n u m num num的节点即可。
void add(int num) {int newLevel = randLevel();vector<SkiplistNode*> update(newLevel, head); // 默认值为headSkiplistNode* p = head;for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {while (p->next[i] && p->next[i]->value < num) { // 每层找最后一个严格小于num的节点p = p->next[i];}if (i < newLevel) { // 只有低newLevel层需要插入p节点update[i] = p;}}level = max(level, newLevel); // 更新跳表最大层数SkiplistNode* newNode = new SkiplistNode(num, newLevel);for (int i = 0; i < newLevel; i++) { // 低newLevel层每层插入新节点newNode->next[i] = update[i]->next[i];update[i]->next[i] = newNode;}
}
删除
删除和新增类似,找到每层需要更新next的节点,更新next并更新层数。
与插入不同的是,在开始遍历前不知道 n u m num num一共有几层,所以我们可以初始化 u p d a t e update update大小为当前跳表的总层数。在真正删除节点时从最下层往最上层删除,一旦update[i]的next不是目标节点了就直接break。
注意,若 n u m num num本身就不再跳表中就不要误删其他元素了。
删除完目标节点后,从上到下遍历确定是否有空层(head的next直接为null)需要删除即可。
bool erase(int num) {vector<SkiplistNode*> update(level); // 其实并不需要初始值SkiplistNode* p = head;for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {while (p->next[i] && p->next[i]->value < num) { // 每层找最后一个严格小于num的节点p = p->next[i];}update[i] = p;}p = p->next[0]; // 目标节点if (!p || p->value != num) { // num在跳表中根本不存在return false;}for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) { // 从下往上开始删除目标节点if (update[i]->next[i] != p) {break;}update[i]->next[i] = p->next[i];}delete p;while (level > 0 && !head->next[level - 1]) { // “移除”空层level--;}return true;
}
时空复杂度
- 时间复杂度:单次操作 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn)
- 空间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
AC代码
C++
const int MAX_LEVEL = 15;
const double p = 0.5;class SkiplistNode {
public:int value;vector<SkiplistNode*> next;SkiplistNode(int val, int level): value(val), next(level) {} // 一个节点一旦生成,level就是固定的
};class Skiplist {
private:SkiplistNode* head;int level;int randLevel() {int ans = 1;while (ans < MAX_LEVEL && rand() < p) {ans++;}return ans;}
public:Skiplist() {head = new SkiplistNode(-1, MAX_LEVEL); // 每层一旦出现,就一定需要head节点level = 0;}bool search(int target) {SkiplistNode* p = head;for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {while (p->next[i] && p->next[i]->value < target) {p = p->next[i];}}p = p->next[0];return p && p->value == target;}void add(int num) {int newLevel = randLevel();vector<SkiplistNode*> update(newLevel, head);SkiplistNode* p = head;for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {while (p->next[i] && p->next[i]->value < num) {p = p->next[i];}if (i < newLevel) {update[i] = p;}}level = max(level, newLevel);SkiplistNode* newNode = new SkiplistNode(num, newLevel);for (int i = 0; i < newLevel; i++) {newNode->next[i] = update[i]->next[i];update[i]->next[i] = newNode;}}bool erase(int num) {vector<SkiplistNode*> update(level);SkiplistNode* p = head;for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {while (p->next[i] && p->next[i]->value < num) {p = p->next[i];}update[i] = p;}p = p->next[0];if (!p || p->value != num) {return false;}for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {if (update[i]->next[i] != p) {break;}update[i]->next[i] = p->next[i];}delete p;while (level > 0 && !head->next[level - 1]) {level--;}return true;}
};/*** Your Skiplist object will be instantiated and called as such:* Skiplist* obj = new Skiplist();* bool param_1 = obj->search(target);* obj->add(num);* bool param_3 = obj->erase(num);*/
Python
from typing import List, Any
import randomMAX_LEVEL = 15
P = 0.5class SkiplistNode:def __init__(self, v: int, level: int):self.value = vself.next: List[SkiplistNode] = [None] * levelclass Skiplist:def __init__(self):self.head = SkiplistNode(-1, MAX_LEVEL)self.level = 0def __randLevel(self):ans = 1while ans < MAX_LEVEL and random.random() < P:ans += 1return ansdef search(self, target: int) -> bool:p = self.headfor i in range(self.level - 1, -1, -1):while p.next[i] and p.next[i].value < target:p = p.next[i]p = p.next[0]# return p and p.value == target # 不可!p为None的化这一行会return None而不是False!return p is not None and p.value == targetdef add(self, num: int) -> None:newLevel = self.__randLevel()update = [self.head] * newLevelp = self.headfor i in range(self.level - 1, -1, -1):while p.next[i] and p.next[i].value < num:p = p.next[i]if i < newLevel:update[i] = pself.level = max(self.level, newLevel)newNode = SkiplistNode(num, newLevel)for i in range(newLevel):newNode.next[i] = update[i].next[i]update[i].next[i] = newNodedef erase(self, num: int) -> bool:update: List[SkiplistNode | Any] = [None] * self.levelp = self.headfor i in range(self.level - 1, -1, -1):while p.next[i] and p.next[i].value < num:p = p.next[i]update[i] = pp = p.next[0]if not p or p.value != num:return Falsefor i in range(self.level):if update[i].next[i] != p:breakupdate[i].next[i] = p.next[i]while self.level > 0 and not self.head.next[self.level - 1]:self.level -= 1return True# Your Skiplist object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = Skiplist()
# param_1 = obj.search(target)
# obj.add(num)
# param_3 = obj.erase(num)
同步发文于CSDN和我的个人博客,原创不易,转载经作者同意后请附上原文链接哦~
千篇源码题解已开源














