目前Isaac Lab支持的强化学习框架
Isaac Lab支持的强化学习框架介绍![]() http://t.csdnimg.cn/h8u7Z调研下来,能够实现字典状态量,也就是多输入状态量的有
http://t.csdnimg.cn/h8u7Z调研下来,能够实现字典状态量,也就是多输入状态量的有
rsl_rl、sb3、(skrl不确定),rl_games是显然不支持的,自己改了一版,花了很长时间,目前训练还不收敛,个人觉得rl_games定制网络和策略不那么友好。rsl_rl关节类的研究对象用这个多一些,但是目前master分支只支持PPO算法,algorithms分支支持算法很多,但是没有合并到master,使用不方便;sb3比较通用一点;rl_games 是 NVIDIA Isaac Gym里官方使用的,skrl比较新官方文档看着很强大。
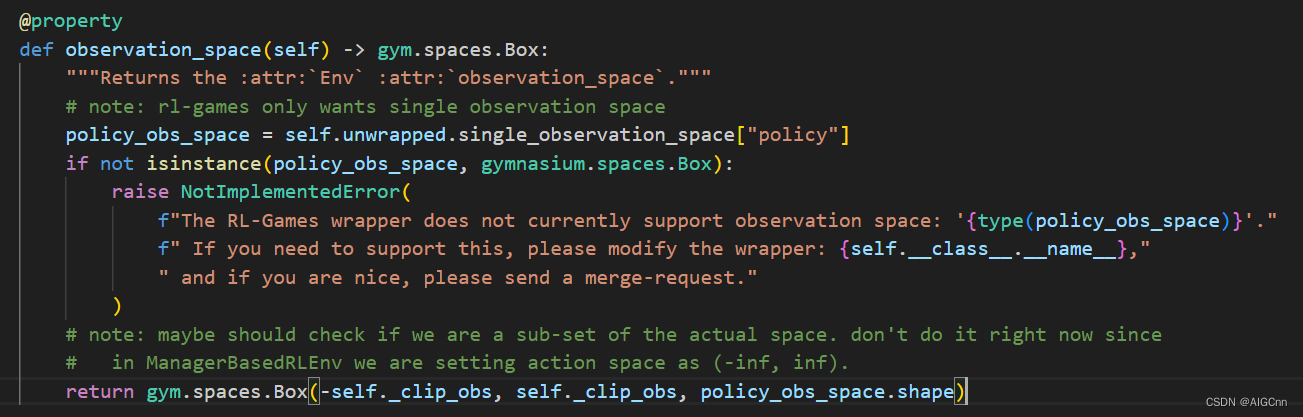
目前Lab里rl_games 的 observation_space 只支持 gym.spaces.Box
如果你想添加新的强化学习框架,可以在这里修改:
omni.isaac.lab_tasks\omni\isaac\lab_tasks\utils\wrappers
Adding your own learning library — Isaac Lab documentation (isaac-sim.github.io)
好了,Stable Baselines3 是直接可以用 ``MultiInputPolicy`` 的
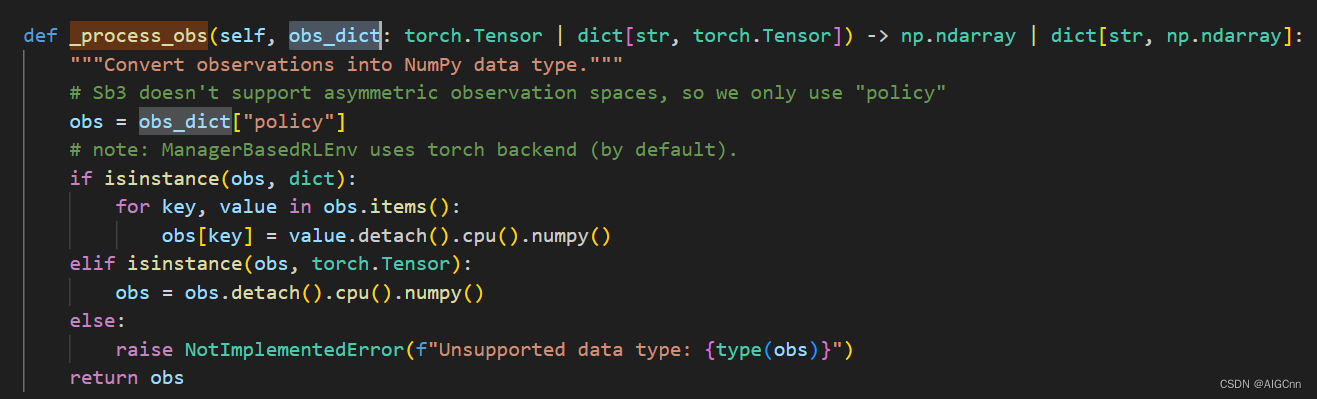
目前Lab里sb3的 observation dict 处理过程
sb3官方对多输入状态量的描述与例子,如图像 + 舵机数据这种,还简单定义了``SimpleMultiObsEnv``演示环境
Dict Observations
You can use environments with dictionary observation spaces. This is useful in the case where one can’t directly concatenate observations such as an image from a camera combined with a vector of servo sensor data (e.g., rotation angles). Stable Baselines3 provides SimpleMultiObsEnv as an example of this kind of setting. The environment is a simple grid world, but the observations for each cell come in the form of dictionaries. These dictionaries are randomly initialized on the creation of the environment and contain a vector observation and an image observation.
Examples — Stable Baselines3 2.4.0a3 documentation (stable-baselines3.readthedocs.io)
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
from stable_baselines3.common.envs import SimpleMultiObsEnv# Stable Baselines provides SimpleMultiObsEnv as an example environment with Dict observations
env = SimpleMultiObsEnv(random_start=False)model = PPO("MultiInputPolicy", env, verbose=1)
model.learn(total_timesteps=100_000)那``MultiInputPolicy``使用的策略网络是什么,Stable Baselines3 支持使用 Dict Gym 空间处理多个输入。这可以使用 MultiInputPolicy 来完成,默认情况下,它使用 CombinedExtractor 特征提取器将多个输入转换为单个向量,由 net_arch 网络处理。具体见1、2、3描述
策略网络 — Stable Baselines3 2.4.0a3 文档 --- Policy Networks — Stable Baselines3 2.4.0a3 documentation (stable-baselines3.readthedocs.io)
Multiple Inputs and Dictionary Observations
By default, CombinedExtractor processes multiple inputs as follows:
默认情况下, CombinedExtractor 按如下方式处理多个输入:
-
If input is an image (automatically detected, see
common.preprocessing.is_image_space), process image with Nature Atari CNN network and output a latent vector of size256.
如果输入是图像(自动检测,请参阅common.preprocessing.is_image_space),则使用Nature Atari CNN网络处理图像并输出大小256为的潜在向量。 -
If input is not an image, flatten it (no layers).
如果输入不是图像,请将其拼合(无图层)。 -
Concatenate all previous vectors into one long vector and pass it to policy.
将所有先前的向量连接成一个长向量,并将其传递给策略。
那么如何来自定义特征提取网络呢?如CNN与MLP以及拼接大小
Much like above, you can define custom features extractors. The following example assumes the environment has two keys in the observation space dictionary: “image” is a (1,H,W) image (channel first), and “vector” is a (D,) dimensional vector. We process “image” with a simple downsampling and “vector” with a single linear layer.
与上面非常相似,您可以定义自定义功能提取器。以下示例假定环境在观测空间字典中有两个键:“image”是 (1,H,W) 图像(通道优先),“vector”是 (D,) 维向量。我们用简单的下采样处理“图像”,用单个线性层处理“矢量”。
import gymnasium as gym
import torch as th
from torch import nnfrom stable_baselines3.common.torch_layers import BaseFeaturesExtractorclass CustomCombinedExtractor(BaseFeaturesExtractor):def __init__(self, observation_space: gym.spaces.Dict):# We do not know features-dim here before going over all the items,# so put something dummy for now. PyTorch requires calling# nn.Module.__init__ before adding modulessuper().__init__(observation_space, features_dim=1)extractors = {}total_concat_size = 0# We need to know size of the output of this extractor,# so go over all the spaces and compute output feature sizesfor key, subspace in observation_space.spaces.items():if key == "image":# We will just downsample one channel of the image by 4x4 and flatten.# Assume the image is single-channel (subspace.shape[0] == 0)extractors[key] = nn.Sequential(nn.MaxPool2d(4), nn.Flatten())total_concat_size += subspace.shape[1] // 4 * subspace.shape[2] // 4elif key == "vector":# Run through a simple MLPextractors[key] = nn.Linear(subspace.shape[0], 16)total_concat_size += 16self.extractors = nn.ModuleDict(extractors)# Update the features dim manuallyself._features_dim = total_concat_sizedef forward(self, observations) -> th.Tensor:encoded_tensor_list = []# self.extractors contain nn.Modules that do all the processing.for key, extractor in self.extractors.items():encoded_tensor_list.append(extractor(observations[key]))# Return a (B, self._features_dim) PyTorch tensor, where B is batch dimension.return th.cat(encoded_tensor_list, dim=1)环境定义,这里使用的是DirectRLEnv;可以参考 cartpole_camera_env.py
添加摄像头:
# camera
tiled_camera: TiledCameraCfg = TiledCameraCfg(prim_path="/World/envs/env_.*/Robot/body/Camera",offset=TiledCameraCfg.OffsetCfg(pos=(0.0, 0.0, 0.05), rot=(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0), convention="ros"),data_types=["rgb"],spawn=sim_utils.PinholeCameraCfg(focal_length=24.0, focus_distance=400.0, horizontal_aperture=20.955, clipping_range=(0.1, 10.0)),width=640,height=480,)由于自定义space,需要重写父类 ``DirectRLEnv`` 方法 _configure_gym_env_spaces,如我这里定义的:
def _configure_gym_env_spaces(self):"""Configure the action and observation spaces for the Gym environment."""# observation space (unbounded since we don't impose any limits)self.num_actions = self.cfg.num_actionsself.num_observations_img = self.cfg.num_observations_imgself.num_observations_vec = self.cfg.num_observations_vecself.num_states = self.cfg.num_states# set up spacesself.single_observation_space = gym.spaces.Dict()self.single_observation_space["policy"] = gym.spaces.Dict()self.single_observation_space["policy"]["img"] = gym.spaces.Box(low=-np.inf, high=np.inf, shape=(self.cfg.tiled_camera.height, self.cfg.tiled_camera.width, self.cfg.num_channels),)self.single_observation_space["policy"]["vec"] = gym.spaces.Box(low=-np.inf, high=np.inf, shape=(self.num_observations_vec,))if self.num_states > 0:self.single_observation_space["critic"] = gym.spaces.Box(low=-np.inf,high=np.inf,shape=(self.num_observations_vec, ),)self.single_action_space = gym.spaces.Box(low=-1.0, high=1.0, shape=(self.num_actions,))# batch the spaces for vectorized environmentsself.observation_space = gym.vector.utils.batch_space(self.single_observation_space, self.num_envs)self.action_space = gym.vector.utils.batch_space(self.single_action_space, self.num_envs)具体 _get_observations 实现 (省略里面具体状态量获取)
def _get_observations(self) -> dict:# 具体 observations 实现observations = {"policy": {"img": self._tiled_camera.data.output[data_type].clone(), "vec": obs}}return observationssb3策略配置,policy 部分为 'MultiInputPolicy'
# Reference: https://github.com/DLR-RM/rl-baselines3-zoo/blob/master/hyperparams/ppo.yml#L32
seed: 42n_timesteps: 20000
policy: 'MultiInputPolicy'
n_steps: 16
batch_size: 64
gae_lambda: 0.95
gamma: 0.99
n_epochs: 10
ent_coef: 0.01
learning_rate: !!float 3e-4
clip_range: !!float 0.2
policy_kwargs: "dict(activation_fn=nn.ELU,net_arch=[256, 256, 256, 128],squash_output=False,)"
vf_coef: 1.0
max_grad_norm: 1.0
device: "cuda:0"
开始训练:
python source/standalone/workflows/sb3/train.py --task=你的智能体名 --headless --enable_camerasPS:
测试发现,Stable Baselines3的训练速度比 rsl_rl 和 rl_games要慢,GPU利用率也低,不知道是不是超参数设置不一样,后续会继续对比;
欢迎加QQ群一起交流学习:723139415








_百度推广优化方案_郑州官网网络营销外包)





