文章目录
- 1. list的介绍及使用
- 1.1 list的介绍
- 1.2 list的使用
- 1.2.1 list的构造
- 1.2.2 list iterator的使用
- 1.2.3 list capacity
- 1.2.4 list element access
- 1.2.5 list modifiers
- push_back 和emplace_back
- inset
- erase
- 1.2.6 Operations:
- reverse (逆置)
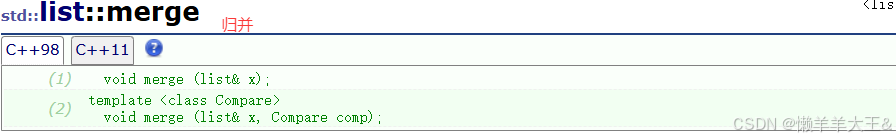
- merg(归并)
- unique(去重)
- remove
- splice
- sort(默认升序) 
- 1.2.7 list的迭代器失效
- 2. list的模拟实现
- 2.1 模拟实现list
- 拓展
- const迭代器
- 3. list与vector的对比
- 本篇文章全部源码
- 总结
1. list的介绍及使用
1.1 list的介绍
list
1.2 list的使用
1.2.1 list的构造
1.2.2 list iterator的使用

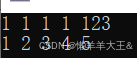
int main()
{list<int> lt1;lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(1);lt1.emplace_back(123);list<int> lt2 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西while (it1 != lt1.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;for (auto e : lt2){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
1.2.3 list capacity
1.2.4 list element access

1.2.5 list modifiers
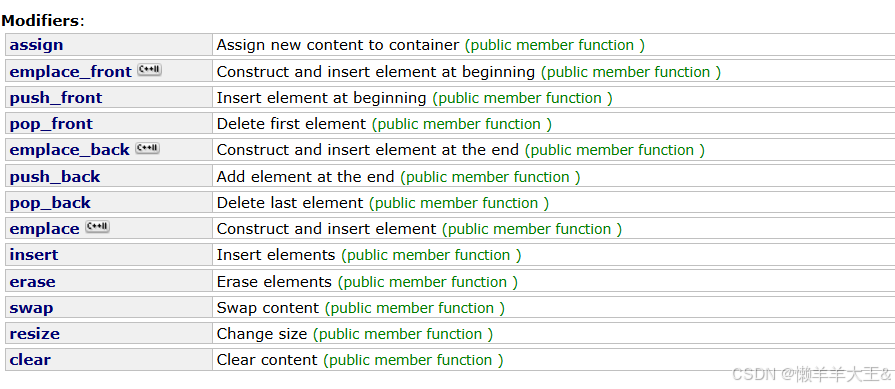
push_back 和emplace_back
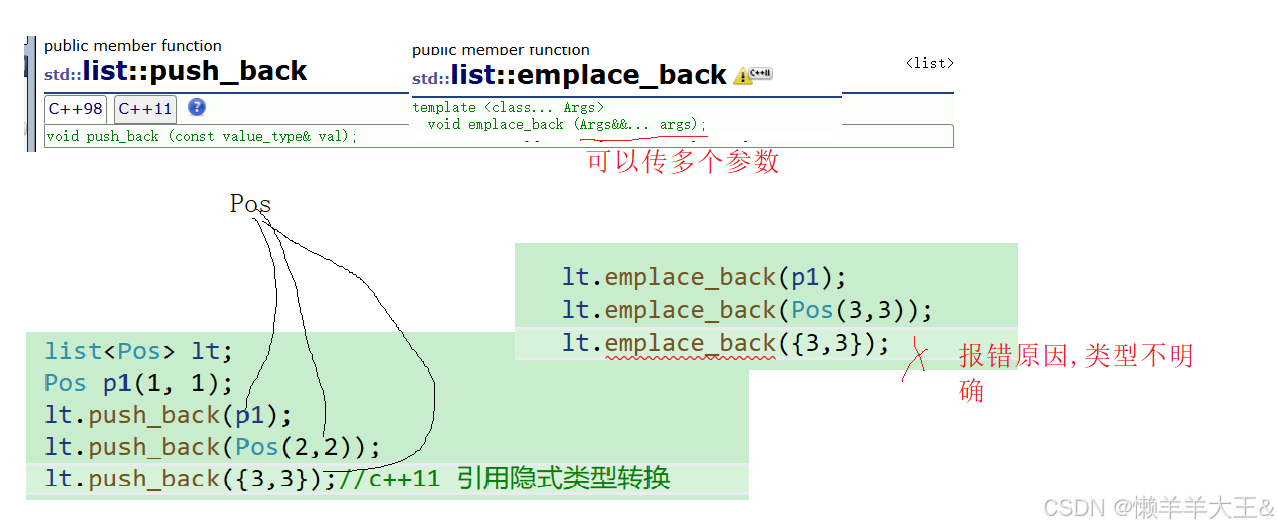
class Pos
{int _row;int _col;
public:Pos(int row, int col)//要大写:_row(row),_col(col){}
};
int main()
{list<Pos> lt;//构造+拷贝构造Pos p1(1, 1);lt.push_back(p1);lt.push_back(Pos(2,2));lt.push_back({3,3});//c++11 引用隐式类型转换lt.emplace_back(p1);lt.emplace_back(Pos(3,3));//lt.emplace_back({ 3,3 });//报错原因不明确//直接构造lt.emplace_back( 3,3 );return 0;
}
inset

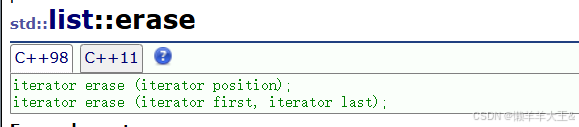
erase
int main()
{list<int> lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;int x;cin >> x;auto it = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(), x);if (it != lt1.end()){lt1.erase(it);}for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}

1.2.6 Operations:
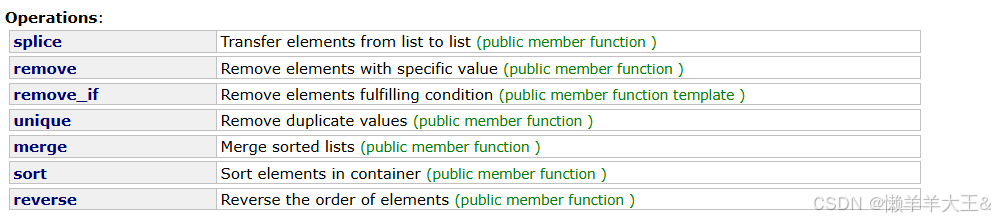
reverse (逆置)

merg(归并)

unique(去重)
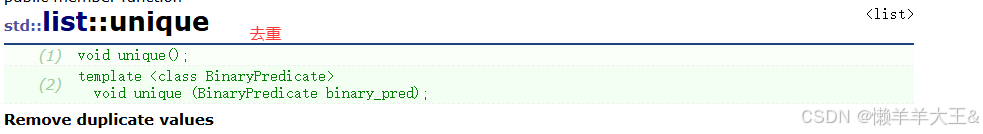
先排完序,再去去重
// list::unique
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <list>// a binary predicate implemented as a function:
bool same_integral_part (double first, double second)
{ return ( int(first)==int(second) ); }// a binary predicate implemented as a class:
struct is_near {bool operator() (double first, double second){ return (fabs(first-second)<5.0); }
};int main ()
{double mydoubles[]={ 12.15, 2.72, 73.0, 12.77, 3.14,12.77, 73.35, 72.25, 15.3, 72.25 };std::list<double> mylist (mydoubles,mydoubles+10);mylist.sort(); // 2.72, 3.14, 12.15, 12.77, 12.77,// 15.3, 72.25, 72.25, 73.0, 73.35mylist.unique(); // 2.72, 3.14, 12.15, 12.77// 15.3, 72.25, 73.0, 73.35mylist.unique (same_integral_part); // 2.72, 3.14, 12.15// 15.3, 72.25, 73.0mylist.unique (is_near()); // 2.72, 12.15, 72.25std::cout << "mylist contains:";for (std::list<double>::iterator it=mylist.begin(); it!=mylist.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';return 0;
}
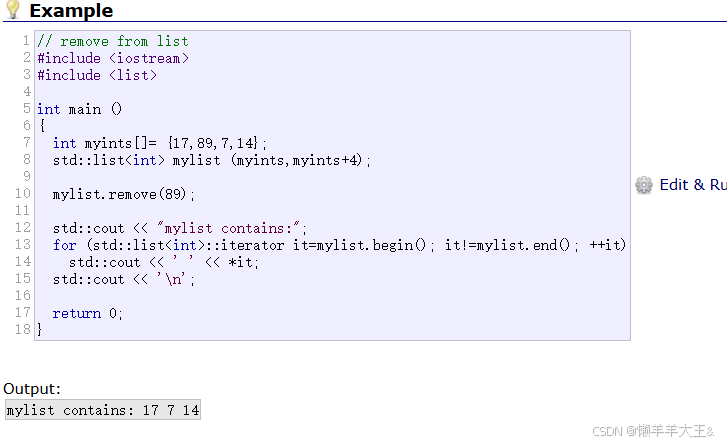
remove

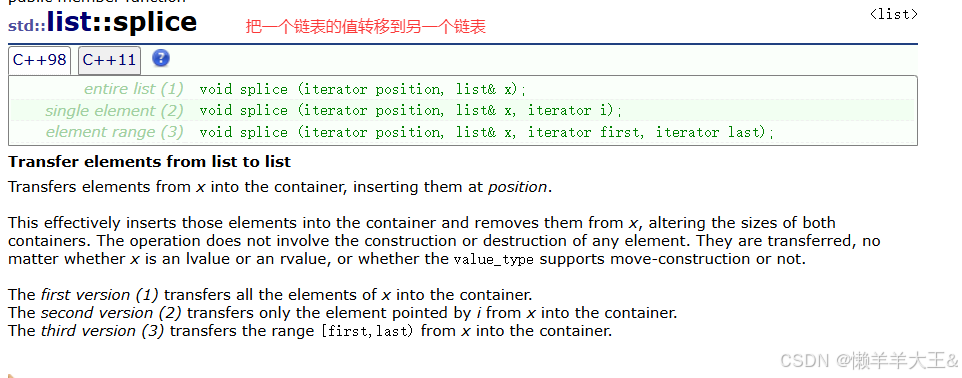
splice

注意:下方代码段while (cin >>x) //在vs中,cin在io流中,按ctrl z 再按回车,结束循环(正常运行) ;ctrl c (失败了)
int main()
{list<int> lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };//LRU 最近访问过的值往调int x;while (cin >>x) //在vs中,cin在io流中,按ctrl z 再按回车,结束循环(正常运行) ;ctrl c (失败了){auto pos = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(), x);if (pos != lt1.end()){lt1.splice(lt1.begin(),lt1,pos);}for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}return 0;
}
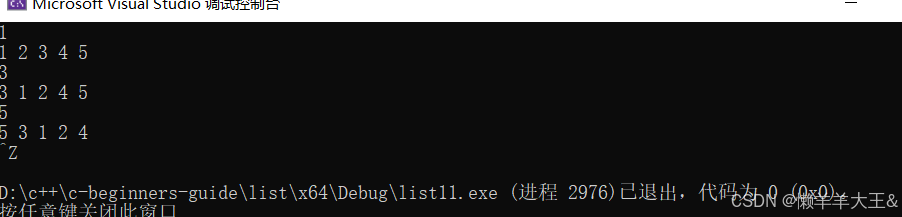
sort(默认升序) 
int main()
{list<int> lt1 = { 1,29,3,4,-1,6 };for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;lt1.sort();//默认升序for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}

int main()
{list<int> lt1 = { 1,29,3,4,-1,6 };for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;//lt1.sort();//默认升序//修改为降序 写法一/*greater<int>gt;lt1.sort(gt);*///修改为降序 写法二lt1.sort(greater<int>());//匿名对象for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
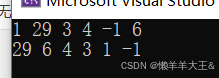
注意:
这里算法库sort和list::sort的区别:
list不可以调用算法库的sort,他只能用他自己的sort;
//排序
int main()
{list<int> lt1 = { 1,29,3,4,-1,6 };for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;//lt1.sort();//默认升序//修改为降序 写法一/*greater<int>gt;lt1.sort(gt);*///修改为降序 写法二//lt1.sort(greater<int>());//匿名对象//for (auto e : lt1)//{// cout << e << " ";//}//cout << endl;vector<int> lt2 = { 1,29,3,4,-1,6 };//sort(lt2.begin(), lt2.end());//sort(lt2.begin(), lt2.end(),greater<int>());//降序sort(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(),greater<int>());//降序for (auto e : lt2){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
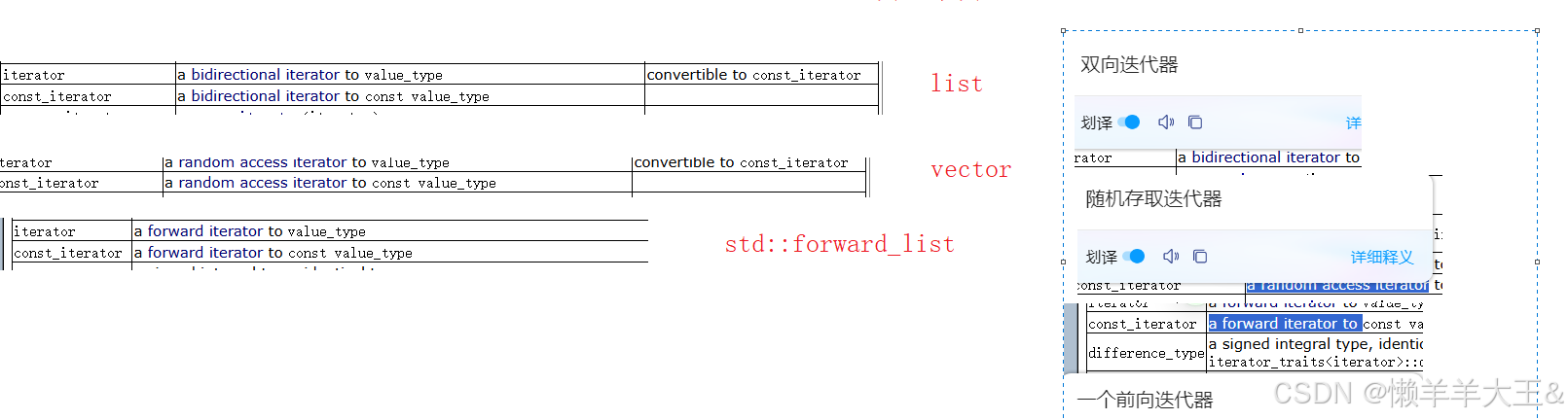
迭代器:
单向迭代器 ++ forwad_list / unordered_xx
双向迭代器 ++/-- list
随机迭代器 ++/–/-/+ string/ vector
有点像继承关系,随机支持双向和单向,双向也单向
判断使用:
1.2.7 list的迭代器失效
迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点的无效,即该节点被删除了。因为list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代器失效的,只有在删除时才会失效,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响。
void TestListIterator1()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array+sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]));
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
// erase()函数执行后,it所指向的节点已被删除,因此it无效,在下一次使用it时,必须先给
其赋值
l.erase(it);
++it;
}
}
// 改正
void TestListIterator()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array+sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]));
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
l.erase(it++); // it = l.erase(it);
}
}
2. list的模拟实现
2.1 模拟实现list
list1.h
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace st {template<class T>//惯例// 全部都是共有,一般用struct、struct list_node //共有{T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node(const T& x = T())//匿名对象使用场景:_data (x), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}};template<class T>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}T&operator*() //T&好处:可读可写{return _node->_data;}T* operator->() {return &_node->_data;}Self&operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator++(int) //后置佳佳{Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->next;return tmp;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator != (const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}};template<class T>class list //既有公用又有私有用class{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}void empty_init(){_head = new Node();_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}list(){empty_init();}void push_back(const T& x){Node* new_node = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = new_node;new_node->_prev = tail;new_node->_next = _head;_head->_prev = new_node;}private:Node* _head;};
}
test.cpp
#include"List1.h"
int main()
{st::list<int> lt1;lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(1);st::list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西while (it1 != lt1.end()){*it1 = 3;cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;st::list<Pos> lt2;//构造+拷贝构造Pos p1(1, 1);lt2.push_back(p1);lt2.push_back(Pos(2,2));lt2.push_back({3,3});//c++11 引用隐式类型转换st::list<Pos>::iterator it2 = lt2.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西while (it2 != lt2.end()){//cout << (*it2)._row << ": " << (*it2)._col << endl;//本质:为了可读性,特殊处理,省略了一个->cout << it2->_row << ": " << it2->_col << endl;//cout << it2.operator->()->_row << ": " << it2.operator->()->_col << endl;++it2;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
拓展

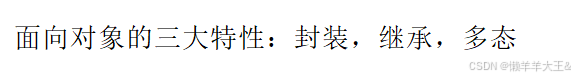
容器迭代器设计思路体现了封装
屏蔽底层实现细节,屏蔽各容器结构的差异,本质封装底层细节和差异,提供统一的访问方式
const迭代器
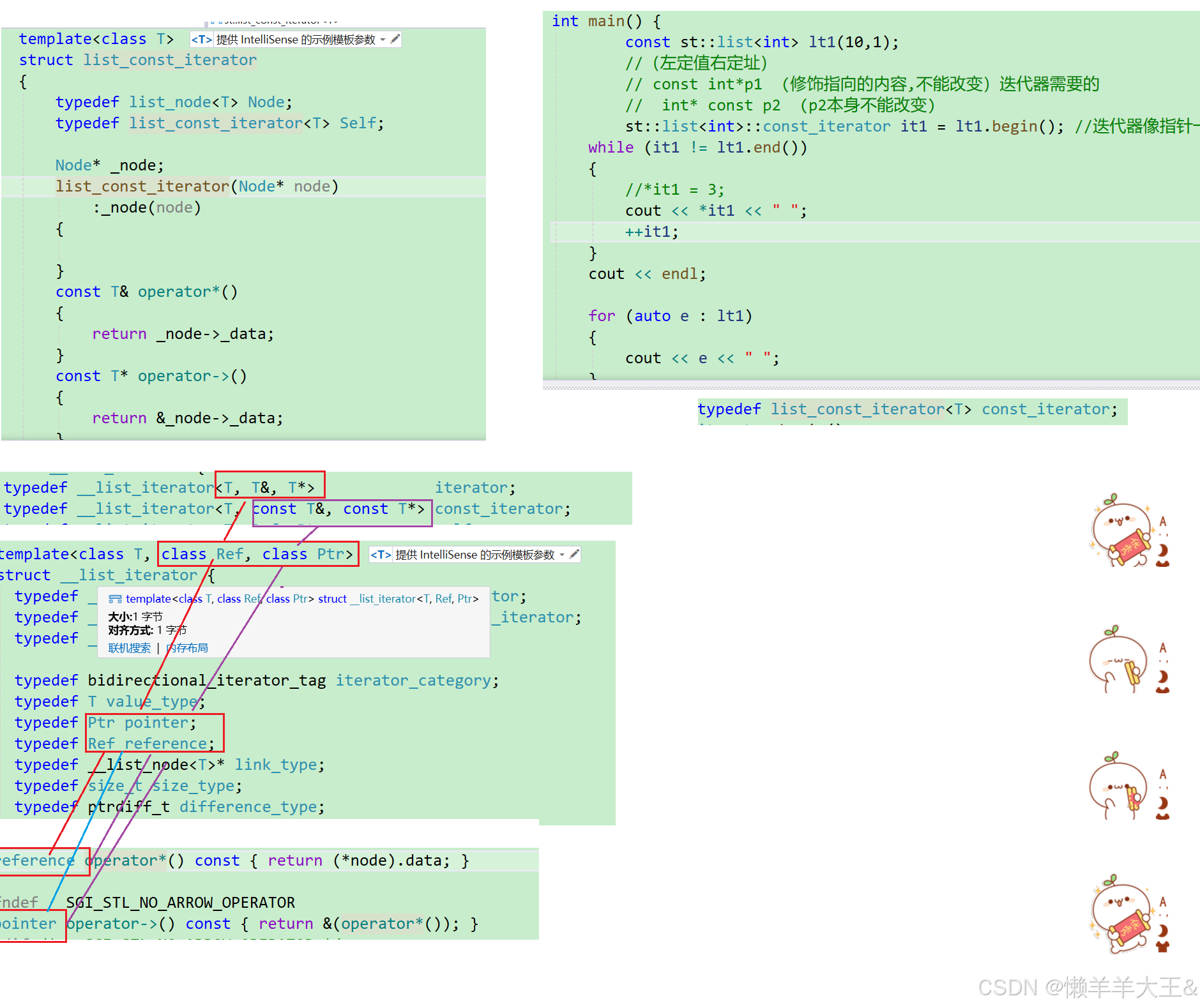
test.cpp
int main() {const st::list<int> lt1(10,1);//(左定值右定址)// const int*p1 (修饰指向的内容,不能改变)迭代器需要的// int* const p2 (p2本身不能改变)st::list<int>::const_iterator it1 = lt1.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西while (it1 != lt1.end()){//*it1 = 3;cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;st::list<Pos> lt2;st::list<Pos>::iterator it2 = lt2.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西while (it2 != lt2.end()){//cout << (*it2)._row << ": " << (*it2)._col << endl;//本质:为了可读性,特殊处理,省略了一个->cout << it2->_row << ": " << it2->_col << endl;//cout << it2.operator->()->_row << ": " << it2.operator->()->_col << endl;++it2;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
list1.h
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*() //T&好处:可读可写{return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->() {return &_node->_data;}Self&operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator++(int) //后置佳佳{Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->next;return tmp;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator != (const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}
};
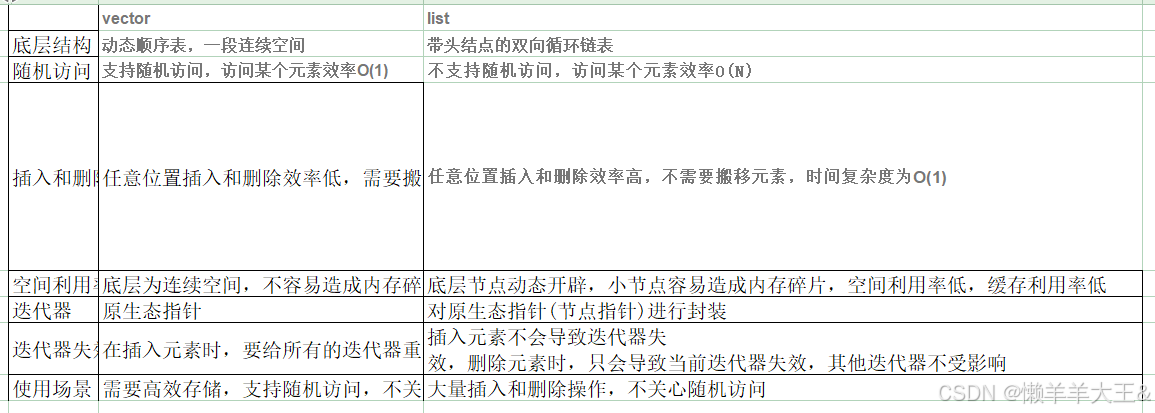
3. list与vector的对比
vector与list都是STL中非常重要的序列式容器,由于两个容器的底层结构不同,导致其特性以及
应用场景不同,其主要不同如下:
本篇文章全部源码
list.h
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace st {template<class T>//惯例// 全部都是共有,一般用struct、struct list_node //共有{T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node(const T& x = T())//匿名对象使用场景:_data (x), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}};template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*() //T&好处:可读可写{return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->() {return &_node->_data;}Self&operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator++(int) //后置佳佳{Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->next;return tmp;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator != (const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}};//template<class T>//struct list_const_iterator//{// typedef list_node<T> Node;// typedef list_const_iterator<T> Self;// Node* _node;// list_const_iterator(Node* node)// :_node(node)// {// }// const T& operator*() // {// return _node->_data;// }// const T* operator->()// {// return &_node->_data;// }// Self& operator++()// {// _node = _node->_next;// return *this;// }// Self& operator--()// {// _node = _node->_prev;// return *this;// }// Self operator++(int) //后置佳佳// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->next;// return tmp;// }// Self operator--(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_prev;// return tmp;// }// bool operator != (const Self& s)// {// return _node != s._node;// }//};template<class T>class list //既有公用又有私有用class{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:/*typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;*/typedef list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}void empty_init(){_head = new Node();_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){empty_init();}//lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto &e:lt)//加&不然就是*{push_back(e);}}//lt2 = lt3;//list<T>& operator= ( list<T>& lt)list& operator=( list lt){swap(lt);//lt2想要return *this;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void swap(list<T>& tmp){std::swap(_head, tmp._head);}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}list(size_t n, const T&val = T()){empty_init();for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++){push_back(val);}}void push_back(const T& x){/*Node* new_node = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = new_node;new_node->_prev = tail;new_node->_next = _head;_head->_prev = new_node;*///哨兵位头结点就是end()insert(end(), x);//复用}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void pop_back(){erase(--end());//末尾也就是哨兵位-1}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev newnode curprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* del = pos._node;Node* prev = del->_prev;Node* next = del->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete del;--_size;return iterator(next);}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};template <class T>void swap(T& a, T& b){T c(a); a = b; b = c;}template <class T>void swap(list<T>& a, list<T>& b){a.swap(b);}
}
test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>//调用算法库
#include<vector>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
//int main()
//{
// list<int> lt1;
// lt1.push_back(1);
// lt1.push_back(1);
// lt1.push_back(1);
// lt1.push_back(1);
// lt1.emplace_back(123);
//
// list<int> lt2 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
//
// list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西
// while (it1 != lt1.end())
// {
// cout << *it1 << " ";
// ++it1;
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// for (auto e : lt2)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// return 0;
//}class Pos
{
public:int _row;int _col;Pos(int row = 0 , int col = 0 )//要大写:_row(row),_col(col){}
};
//int main()
//{
// list<Pos> lt;
// //构造+拷贝构造
// Pos p1(1, 1);
// lt.push_back(p1);
// lt.push_back(Pos(2,2));
// lt.push_back({3,3});//c++11 引用隐式类型转换
//
// lt.emplace_back(p1);
// lt.emplace_back(Pos(3,3));
// //lt.emplace_back({ 3,3 });//报错原因不明确
// //直接构造
// lt.emplace_back( 3,3 );
//
//
//
// return 0;
//}//int main()
//{
// list<int> lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
// for (auto e : lt1)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// int x;
// cin >> x;
// auto it = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(), x);
// if (it != lt1.end())
// {
// lt1.erase(it);
// }
// for (auto e : lt1)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}//int main()
//{
// list<int> lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
// //LRU 最近访问过的值往调
// int x;
// while (cin >>x) //在vs中,cin在io流中,按ctrl z 再按回车,结束循环(正常运行) ;ctrl c (失败了)
// {
// auto pos = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(), x);
// if (pos != lt1.end())
// {
// lt1.splice(lt1.begin(),lt1,pos);
// }
// for (auto e : lt1)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// }
//
//
// return 0;
//}排序
//int main()
//{
// list<int> lt1 = { 1,29,3,4,-1,6 };
// for (auto e : lt1)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// //lt1.sort();//默认升序
// //修改为降序 写法一
// /*greater<int>gt;
// lt1.sort(gt);*/
// //修改为降序 写法二
// //lt1.sort(greater<int>());//匿名对象
// //for (auto e : lt1)
// //{
// // cout << e << " ";
// //}
// //cout << endl;
//
// vector<int> lt2 = { 1,29,3,4,-1,6 };
// //sort(lt2.begin(), lt2.end());
// //sort(lt2.begin(), lt2.end(),greater<int>());//降序
// sort(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(),greater<int>());//降序
//
// for (auto e : lt2)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// for (auto e : lt1)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
#include"List1.h"
//int main()
//{
// st::list<int> lt1;
// lt1.push_back(1);
// lt1.push_back(1);
// lt1.push_back(1);
// lt1.push_back(1);
// st::list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西
// while (it1 != lt1.end())
// {
// *it1 = 3;
// cout << *it1 << " ";
// ++it1;
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// for (auto e : lt1)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// st::list<Pos> lt2;
// //构造+拷贝构造
// Pos p1(1, 1);
// lt2.push_back(p1);
// lt2.push_back(Pos(2,2));
// lt2.push_back({3,3});//c++11 引用隐式类型转换
//
// st::list<Pos>::iterator it2 = lt2.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西
// while (it2 != lt2.end())
// {
// //cout << (*it2)._row << ": " << (*it2)._col << endl;
// //本质:为了可读性,特殊处理,省略了一个->
// cout << it2->_row << ": " << it2->_col << endl;
// //cout << it2.operator->()->_row << ": " << it2.operator->()->_col << endl;
// ++it2;
// }
// cout << endl;
// return 0;
//}//int main() {
// const st::list<int> lt1(10,1);
// //(左定值右定址)
// // const int*p1 (修饰指向的内容,不能改变)迭代器需要的
// // int* const p2 (p2本身不能改变)
// st::list<int>::const_iterator it1 = lt1.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西
// while (it1 != lt1.end())
// {
// //*it1 = 3;
// cout << *it1 << " ";
// ++it1;
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// for (auto e : lt1)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// st::list<Pos> lt2;
//
//
//
// st::list<Pos>::iterator it2 = lt2.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西
// while (it2 != lt2.end())
// {
// //cout << (*it2)._row << ": " << (*it2)._col << endl;
// //本质:为了可读性,特殊处理,省略了一个->
// cout << it2->_row << ": " << it2->_col << endl;
// //cout << it2.operator->()->_row << ": " << it2.operator->()->_col << endl;
// ++it2;
// }
// cout << endl;
// return 0;
//}//int main()
//{
// st::list<int> lt1;
// lt1.push_back(1);
// lt1.push_back(2);
// lt1.push_back(3);
// lt1.push_back(4);
// lt1.push_front(0);//头插
// lt1.push_front(4);
// st::list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin(); //迭代器像指针一样的东西
// while (it1 != lt1.end())
// {
// cout << *it1 << " ";
// ++it1;
// }
// cout << endl;
// lt1.pop_front();//头删
// lt1.pop_front();
// lt1.pop_back();//尾删
// for (auto e : lt1)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// //拷贝构造
// st::list<int> lt2(lt1);//浅拷贝,程序会崩溃
// for (auto e : lt2)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// st::list<int> lt3(10,1);//赋值
// lt2 = lt3;
// for (auto e : lt2)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// return 0;
//}int main()
{st::list<int> lt1;lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(2);lt1.push_back(3);lt1.push_back(4);lt1.push_front(0);//头插lt1.push_front(4);st::list<int> lt2(10,1);/*lt1.swap(lt2);for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;*/int i = 1, j = 2;
st::swap(i, j);
st::swap(lt1,lt2);for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl; for (auto e : lt2){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl; return 0;
}
总结
以上就是list的使用及模拟实现的全部内容了。喜欢博主写的文章可以一键三连支持博主!!!








_百度推广优化方案_郑州官网网络营销外包)



