基于 PyTorch 的模型量化、剪枝和蒸馏
- 1. 模型量化
- 1.1 原理介绍
- 1.2 PyTorch 实现
- 2. 模型剪枝
- 2.1 原理介绍
- 2.2 PyTorch 实现
- 3. 模型蒸馏
- 3.1 原理介绍
- 3.2 PyTorch 实现
- 参考文献
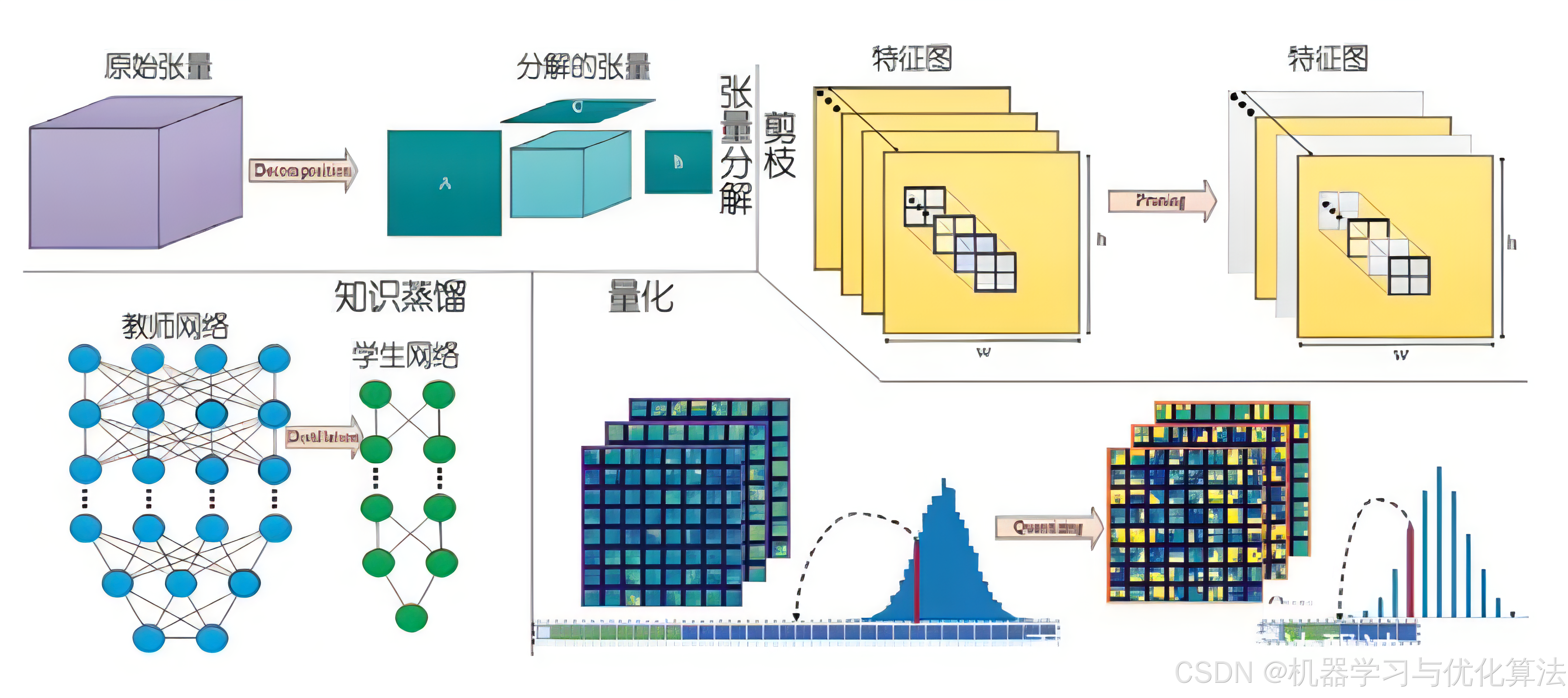
1. 模型量化
1.1 原理介绍
模型量化是将模型参数从高精度(通常是 float32)转换为低精度(如 int8 或更低)的过程。这种技术可以显著减少模型大小、降低计算复杂度,并加快推理速度,同时尽可能保持模型的性能。

量化的主要方法包括:
-
动态量化:
- 在推理时动态地将权重从 float32 量化为 int8。
- 激活值在计算过程中保持为浮点数。
- 适用于 RNN 和变换器等模型。
-
静态量化:
- 在推理之前,预先将权重从 float32 量化为 int8。
- 在推理过程中,激活值也被量化。
- 需要校准数据来确定激活值的量化参数。
-
量化感知训练(QAT):
- 在训练过程中模拟量化操作。
- 允许模型适应量化带来的精度损失。
- 通常能够获得比后量化更高的精度。
1.2 PyTorch 实现
import torch# 1. 动态量化
model_fp32 = MyModel()
model_int8 = torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic(model_fp32, # 原始模型{torch.nn.Linear, torch.nn.LSTM}, # 要量化的层类型dtype=torch.qint8 # 量化后的数据类型
)# 2. 静态量化
model_fp32 = MyModel()
model_fp32.eval() # 设置为评估模式# 设置量化配置
model_fp32.qconfig = torch.quantization.get_default_qconfig('fbgemm')
model_fp32_prepared = torch.quantization.prepare(model_fp32)# 使用校准数据进行校准
with torch.no_grad():for batch in calibration_data:model_fp32_prepared(batch)# 转换模型
model_int8 = torch.quantization.convert(model_fp32_prepared)# 3. 量化感知训练
model_fp32 = MyModel()
model_fp32.train() # 设置为训练模式# 设置量化感知训练配置
model_fp32.qconfig = torch.quantization.get_default_qat_qconfig('fbgemm')
model_fp32_prepared = torch.quantization.prepare_qat(model_fp32)# 训练循环
for epoch in range(num_epochs):for batch in train_data:output = model_fp32_prepared(batch)loss = criterion(output, target)loss.backward()optimizer.step()# 转换模型
model_int8 = torch.quantization.convert(model_fp32_prepared)
2. 模型剪枝
2.1 原理介绍
模型剪枝是一种通过移除模型中不重要的权重或神经元来减少模型复杂度的技术。剪枝可以减少模型大小、降低计算复杂度,并可能改善模型的泛化能力。

主要的剪枝方法包括:
-
权重剪枝:
- 移除绝对值小于某个阈值的单个权重。
- 可以大幅减少模型参数数量,但可能导致非结构化稀疏性。
-
结构化剪枝:
- 移除整个卷积核、神经元或通道。
- 产生更加规则的稀疏结构,有利于硬件加速。
-
重要性剪枝:
- 基于权重或激活值的重要性评分来决定剪枝对象。
- 常用的重要性度量包括权重幅度、激活值、梯度等。
2.2 PyTorch 实现
import torch
import torch.nn.utils.prune as prunemodel = MyModel()# 1. 权重剪枝
prune.l1_unstructured(model.conv1, name='weight', amount=0.3)# 2. 结构化剪枝
prune.ln_structured(model.conv1, name='weight', amount=0.5, n=2, dim=0)# 3. 全局剪枝
parameters_to_prune = ((model.conv1, 'weight'),(model.conv2, 'weight'),(model.fc1, 'weight'),
)
prune.global_unstructured(parameters_to_prune,pruning_method=prune.L1Unstructured,amount=0.2
)# 4. 移除剪枝
for module in model.modules():if isinstance(module, torch.nn.Conv2d):prune.remove(module, 'weight')
3. 模型蒸馏
3.1 原理介绍
模型蒸馏是一种将复杂模型(教师模型)的知识转移到简单模型(学生模型)的技术。这种方法可以在保持性能的同时,大幅减少模型的复杂度和计算需求。

主要的蒸馏方法包括:
-
响应蒸馏:
- 学生模型学习教师模型的最终输出(软标签)。
- 软标签包含了教师模型对不同类别的置信度信息。
-
特征蒸馏:
- 学生模型学习教师模型的中间层特征。
- 可以传递更丰富的知识,但需要设计合适的映射函数。
-
关系蒸馏:
- 学习样本之间的关系,如相似度或排序。
- 有助于保持教师模型学到的数据结构。
3.2 PyTorch 实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as Fclass DistillationLoss(nn.Module):def __init__(self, alpha=0.5, temperature=2.0):super().__init__()self.alpha = alphaself.T = temperaturedef forward(self, student_outputs, teacher_outputs, labels):# 硬标签损失hard_loss = F.cross_entropy(student_outputs, labels)# 软标签损失soft_loss = F.kl_div(F.log_softmax(student_outputs / self.T, dim=1),F.softmax(teacher_outputs / self.T, dim=1),reduction='batchmean') * (self.T * self.T)# 总损失loss = (1 - self.alpha) * hard_loss + self.alpha * soft_lossreturn loss# 训练循环
teacher_model = TeacherModel().eval()
student_model = StudentModel().train()
distillation_loss = DistillationLoss(alpha=0.5, temperature=2.0)for epoch in range(num_epochs):for batch, labels in train_loader:optimizer.zero_grad()with torch.no_grad():teacher_outputs = teacher_model(batch)student_outputs = student_model(batch)loss = distillation_loss(student_outputs, teacher_outputs, labels)loss.backward()optimizer.step()
通过这些技术的组合使用,可以显著减小模型大小、提高推理速度,同时尽可能保持模型性能。在实际应用中,可能需要根据具体任务和硬件限制来选择和调整这些方法。
参考文献
[1]Jacob, B., Kligys, S., Chen, B., Zhu, M., Tang, M., Howard, A., Adam, H., & Kalenichenko, D. (2018). Quantization and Training of Neural Networks for Efficient Integer-Arithmetic-Only Inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (pp. 2704-2713).[2]Krishnamoorthi, R. (2018). Quantizing deep convolutional networks for efficient inference: A whitepaper. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.08342.[3]Han, S., Pool, J., Tran, J., & Dally, W. (2015). Learning both Weights and Connections for Efficient Neural Network. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) (pp. 1135-1143).[4]Li, H., Kadav, A., Durdanovic, I., Samet, H., & Graf, H. P. (2016). Pruning Filters for Efficient ConvNets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.08710.[5]Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., & Dean, J. (2015). Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1503.02531.[6]Romero, A., Ballas, N., Kahou, S. E., Chassang, A., Gatta, C., & Bengio, Y. (2014). FitNets: Hints for Thin Deep Nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6550.
创作不易,烦请各位观众老爷给个三连,小编在这里跪谢了!















