栈(Stack)和队列(Queue)是两种常见的数据结构,广泛应用于计算机科学中。它们的主要区别在于数据的存取方式。
栈(Stack)
定义:
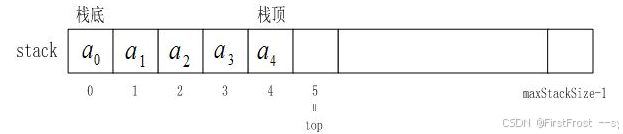
栈是一种遵循''后进先出(LIFO, Last In First Out)"原则的线性数据结构。其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
操作:
-
Push(入栈):将元素添加到栈的顶部。
-
Pop(出栈):移除并返回栈顶的元素。
-
Peek/Top(查看栈顶元素):返回栈顶元素但不移除它。
-
isEmpty(判断栈是否为空):检查栈是否为空。
-
Size(获取栈的大小):返回栈中元素的数量。

栈的实现

Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>// 下面是定长的静态栈的结构,实际中一般不实用
typedef int STDataType;
#define N 10
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType _a[N];int _top; // 栈顶
}Stack;typedef int STDataType;typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;// 初始化和销毁
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);// 入栈 出栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);// 取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);// 判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
// 获取数据个数
int STSize(ST* pst);Stack.c
#include"Stack.h"// 初始化和销毁
void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;// top指向栈顶数据的下一个位置pst->top = 0;// top指向栈顶数据//pst->top = -1;pst->capacity = 0;
}void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}// 入栈 出栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);// 扩容if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}// 取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}// 判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top == 0;
}// 获取数据个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}队列(Queue)
定义:
队列是一种遵循 "先进先出(FIFO, First In First Out )"原则的线性数据结构。最先进入队列的元素最先被取出。
操作:
-
Enqueue(入队):将元素添加到队列的尾部。
-
Dequeue(出队):移除并返回队列头部的元素。
-
Front(查看队头元素):返回队头元素。
-
Rear(查看队尾元素):返回队尾元素。
-
isEmpty(判断队列是否为空):检查队列是否为空。
-
Size(获取队列的大小):返回队列中元素的数量。

Queue的实现
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType val;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* phead;QNode* ptail;int size;
}Queue;void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);// 取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);队尾插入
//void QueuePush(QNode** pphead, QNode** pptail, QDataType x);队头删除
//void QueuePop(QNode** pphead, QNode** pptail);Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->phead;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->next = NULL;newnode->val = x;if (pq->ptail == NULL){pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->size != 0);/*QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;if (pq->phead == NULL)pq->ptail = NULL;*/// 一个节点if (pq->phead->next == NULL){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;}else // 多个节点{QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;}pq->size--;
}QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->phead);return pq->phead->val;
}QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->ptail);return pq->ptail->val;
}int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;
}栈与队列的区别
| 特性 | 栈(Stack) | 队列(Queue) |
|---|---|---|
| 存取原则 | 后进先出(LIFO) | 先进先出(FIFO) |
| 主要操作 | Push, Pop | Enqueue, Dequeue |
| 应用场景 | 函数调用、撤销操作、DFS | 任务调度、BFS、消息队列 |
总结
-
栈适用于需要后进先出的场景,如函数调用和撤销操作。
-
队列适用于需要先进先出的场景,如任务调度和广度优先搜索。
栈和队列例题
1.20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode)
//C++
class Solution {
public:bool isValid(string s) {stack<char> st;auto it = s.begin();while(it != s.end()){if(*it == '(' || *it == '{' || *it == '['){st.push(*it);}else{if(st.empty()){return false;}else{char top = st.top();st.pop();if((top=='('&&*s!=')')||(top=='['&&*s!=']')||(top=='{'&&*s!='}')){return false;} }}it++;}bool ret = st.empty();return ret;}
};//C
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* _a;int _top; // 栈顶int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);//初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->_a = NULL;ps->_capacity = ps->_top = 0;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{assert(ps);if (ps->_top == ps->_capacity){int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->_capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a, newcapacity*sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail!");exit(1);}ps->_capacity = newcapacity;ps->_a = tmp;}ps->_a[ps->_top++] = data;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->_top > 0);ps->_top--;
}
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->_top > 0);return ps->_a[ps->_top-1];
}
//获取栈中
//有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->_top;
}
//检测栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->_top == 0;
}
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->_a);ps->_a = NULL;ps->_capacity = ps->_top = 0;
}bool isValid(char* s)
{Stack st;StackInit(&st);while(*s){if(*s=='('||*s=='{'||*s=='['){//左括号入栈StackPush(&st,*s);}else{//左括号不存在 肯定不能匹配if(StackEmpty(&st)){return false;}//左括号和右括号匹配char top=StackTop(&st);StackPop(&st);if((top=='('&&*s!=')')||(top=='['&&*s!=']')||(top=='{'&&*s!='}')){StackDestroy(&st);return false;}}++s;}//为空说明左括号和右括号匹配完全 返回true 不为空说明还有左括号不能与右括号进行匹配 返回falsebool ret =StackEmpty(&st);StackDestroy(&st);return ret;
}2.225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
3.232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
C语言:栈实现队列 队列实现栈-CSDN博客
4.622. 设计循环队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
typedef struct {int* a;int head;int tail;int k;
} MyCircularQueue;MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));//多开一个空间 解决空和满冲突的问题obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));obj->head=obj->tail=0;obj->k=k;return obj;
}bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {return obj->head==obj->tail;
}bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {return (obj->tail + 1) % (obj->k + 1) == obj -> head;
}bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)){return false;}obj->a[obj->tail]=value;obj->tail++;obj->tail %=(obj->k + 1);return true;
}bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return false;}obj->head++;obj->head %=(obj->k + 1);return true;
}int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}return obj->a[obj->head] ;
}int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}return obj->tail == 0 ? obj->a[obj->k] : obj->a[obj->tail-1];
}void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {free(obj->a);free(obj);
}/*** Your MyCircularQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:* MyCircularQueue* obj = myCircularQueueCreate(k);* bool param_1 = myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, value);* bool param_2 = myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);* int param_3 = myCircularQueueFront(obj);* int param_4 = myCircularQueueRear(obj);* bool param_5 = myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj);* bool param_6 = myCircularQueueIsFull(obj);* myCircularQueueFree(obj);
*/















