Mybatis:一种持久层的框架(集成简化jdbc的操作)解决Dao层
maven的使用:
提供了一套标准化的目录结构
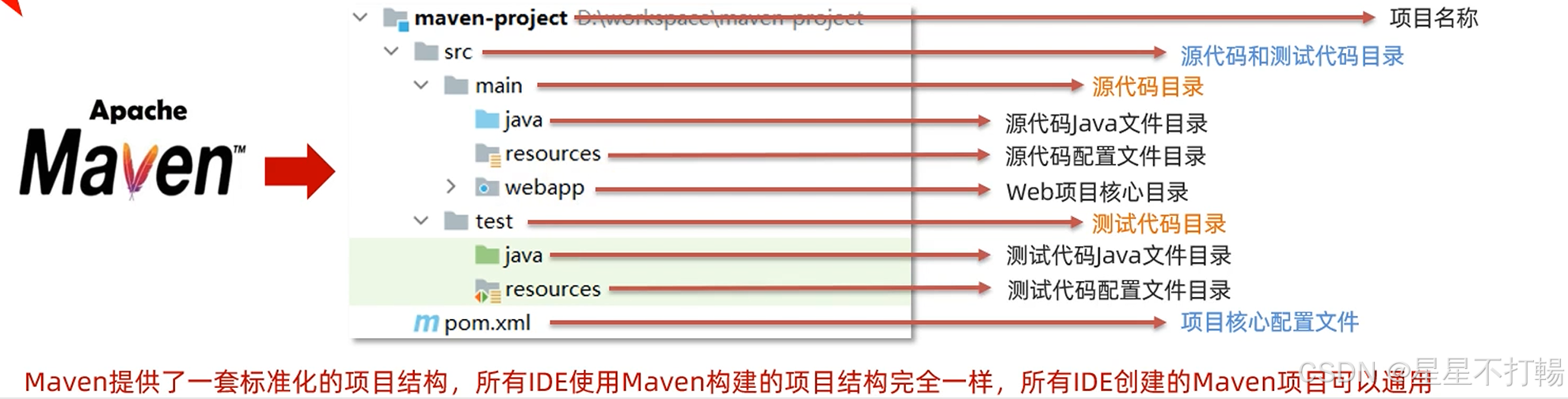
通过导入相关依赖替代导入jar包的操作

Mybatis的整体的框架结构:
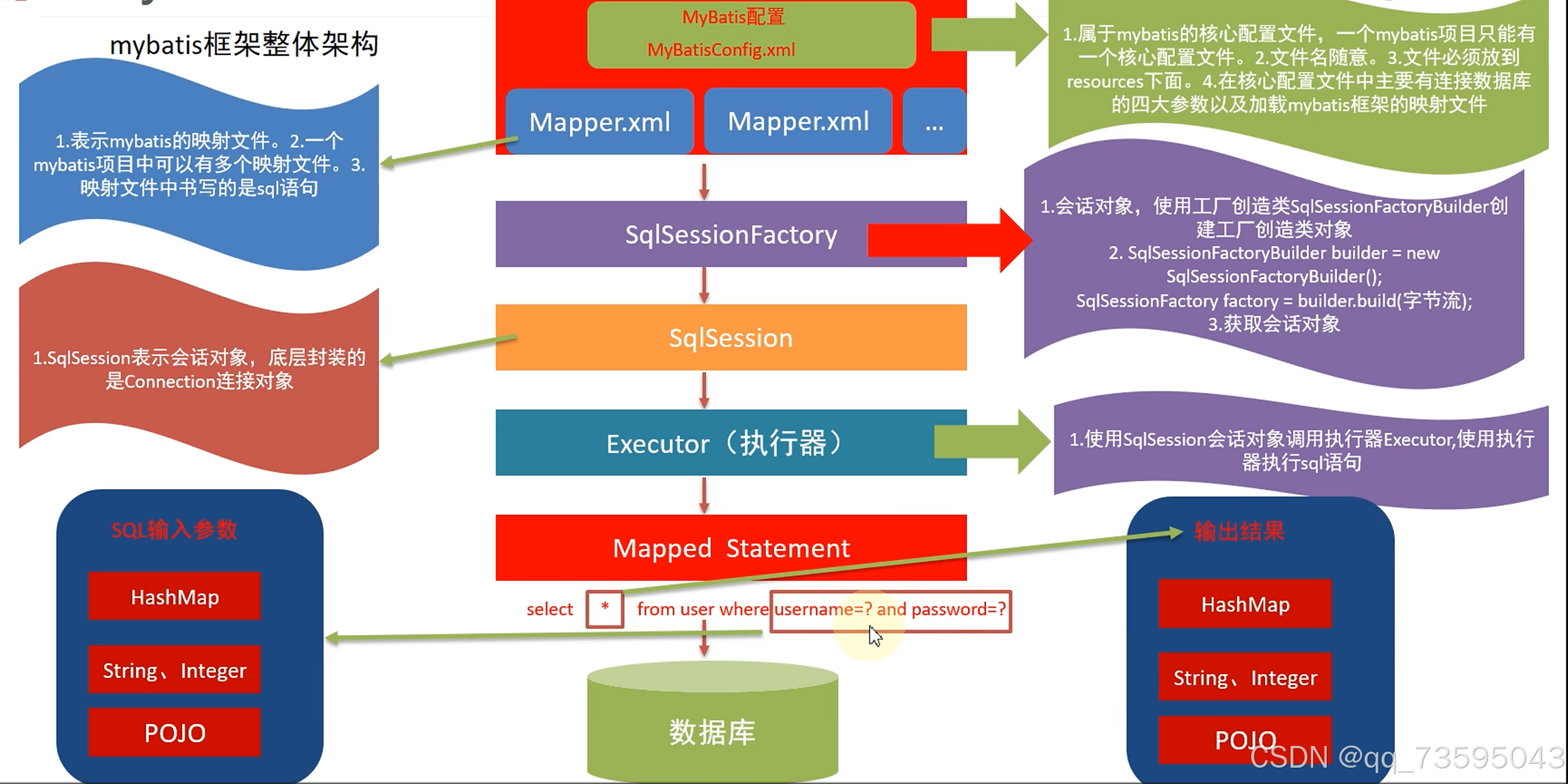
1、两种配置文件:
一个核心配置文件(mybatis-comfig.xml)
多个SQL的映射文件(XxxMapper.xml)
2、有一个SqlSessionFactory工厂对象用于创建SqlSession对象
3、通过SqlSession对象的Executor执行器执行Sql语句
mybatis的ORM映射机制(对象关系映射)
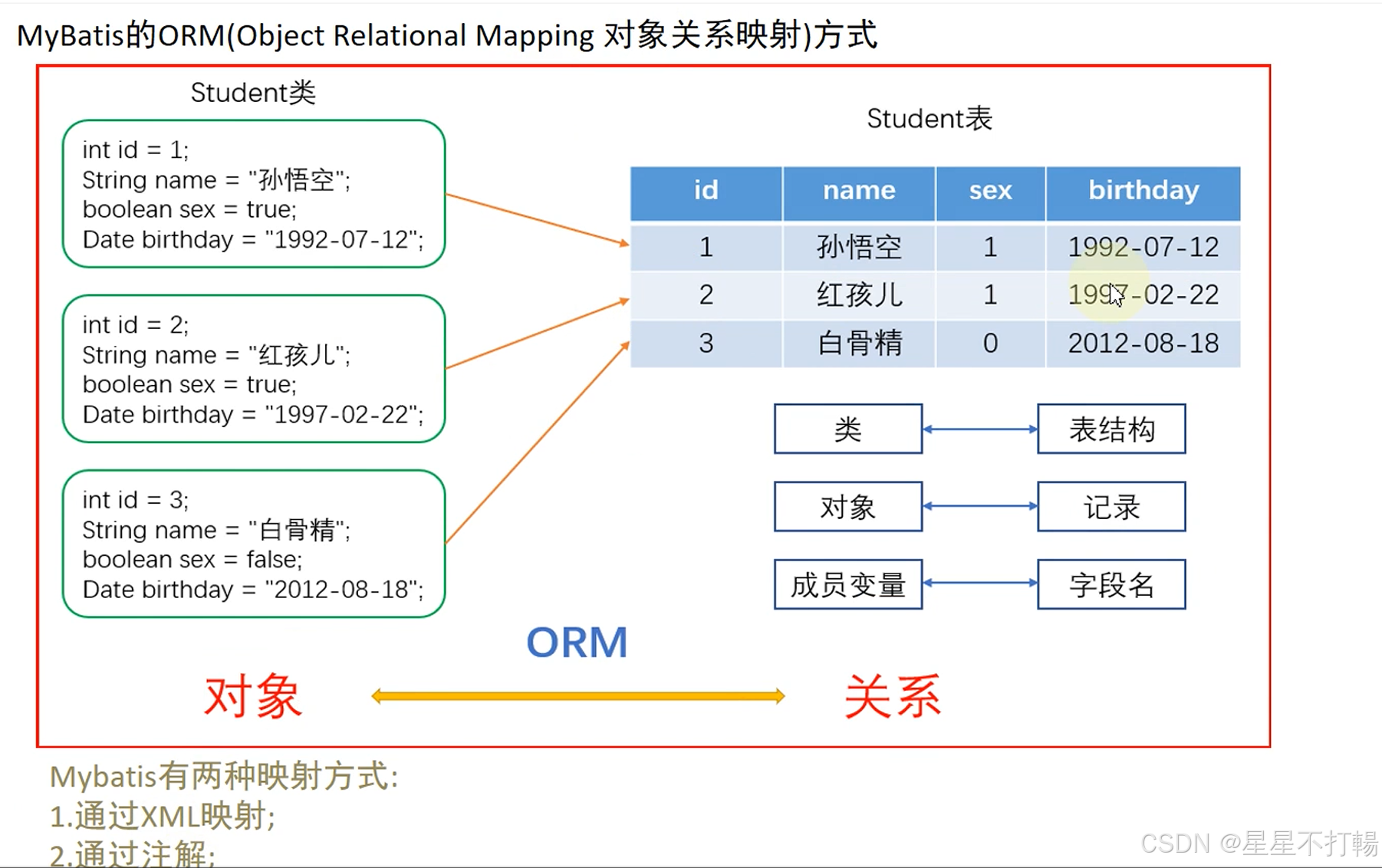
一个Java类对应的表结构
一个实例化对象对应的是表中的一条记录
一个成员变量对应的是表结构的字段名
Mybatis项目工程步骤:
1、核心配置文件:配置数据库的连接参数,配置,映射文件关联参数
mybatis-config.xml(官方模板)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration><environments default="development"><environment id="development"><transactionManager type="JDBC"/><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${driver}"/><property name="url" value="${url}"/><property name="username" value="${username}"/><property name="password" value="${password}"/></dataSource></environment></environments><mappers><mapper resource="org/mybatis/example/BlogMapper.xml"/></mappers>
</configuration>
2、映射配置文件 Xxxmapper.xml :编写相应的SQL代码
(定义与SQL映射文件同名的Mapper接口,
并且保证Mapper接口和SQL映射文件放在同一个目录下)
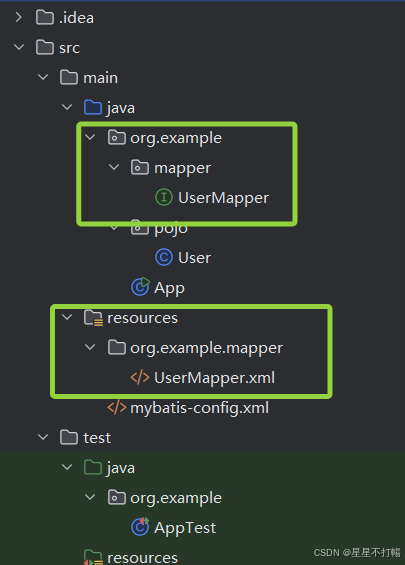
(1)在mapper标签中通过设置namespace属性设置绑定的Mapper接口
(2)在SQL标签中设置
id表示对应的是Mapper接口中的方法名字
resultType:表示返回的结果类型
UserMapper.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><!-- 通过namespace属性绑定当前映射文件与Mapper接口 -->
<mapper namespace="org.example.mapper.UserMapper"><!-- Sql查询语句id:表示当前的sql语句的id->对应的是Mapper接口中的方法名字resultType:表示返回的结果类型--><select id="findAll" resultType="org.example.pojo.User" >select id,username,birthday,sex,address from user</select>
</mapper>
UserMapper.java
public interface UserMapper {/*** 查询所有用户*/public List<User> findAll();
}3、调用Mybatis中的API
解析mybatis的核心配置文件
1、properties标签:通过属性resource:指明文件来源路径
<!-- 引入外部的资源配置文件 -->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>
直接把jdbc.properties文件放在resources目录下
对于properties文件内容的引用通过${key}的方式引入外部资源文件中的数据
jdbc.properties:
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456
引用示例:
<dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/><property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/><property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
2、settings
注意点:当数据表中的字段名与实体类的变量名不一致的时候会发生异常,导致无法通过SQL语句查询到相应的数据,查询出来的结果为null
(例如:user表中的user_name字段然而定义的User实体类的成员变量为username)
解决方法一:在书写SQL语句的时候通过起别名的形式
User.java
public class User {private Integer id;private String username;private Date birthday;private String sex;private String address;
}
UserMapper.xml
<select id="findAll" resultType="org.example.pojo.User" >select id,user_name as username,birthday,sex,address from user
</select>
解决方式二:
通过settings标签在mybatis-config.xml中进行配置(开启驼峰命名法转换:把数据表中的带有下划线的字段。变为Java的驼峰命名法)
例如:字段为user_name,在Java中变为userName或者username
<settings><!-- 开启驼峰命名法转换:把数据表中的带有下划线的字段。变为Java的驼峰命名法:字段为user_name,在Java中变为userName或者username--><setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
解决方式三:通过指定select标签的resultMap属性
<resultMap id="BrandMap" type="com.example.pojo.Brand"><!-- id配置的是数据表中主键字段和实体类的属性映射 --><id property="id" column="id"/><!-- result配置的是数据表中非主键字段和实体类的属性映射 --><result property="brandName" column="brand_name"/><result property="companyName" column="company_name"/><!-- 后面的可以不用再配置了,因为对应的字段名和实体类的属性名是一致的 --><!-- <result property="ordered" column="ordered"/> -->
</resultMap>
<select id="findAllBrand" resultMap="BrandMap">select id,brand_name,company_name,ordered,description,statusfrom tb_brand
</select>
3、mappers标签:建立映射联系(通过Resource属性关联指定对应的Mapper接口)
两种方式:
一、通过指定关联的映射文件
<!-- 方式一:通过指定关联的映射文件--><mapper resource="org/example/dao/UserMapper.xml"/>
二、通过关联Mapper接口扫描Mapper接口包(要求是映射文件,接口文件的类路径在同一个目录下)
<!-- 方式二:通过指定关联的Mapper接口,通过扫描对应的Mapper包 --><package name="org.example.mapper"/>
4、typeAliases标签(package子标签指定要扫描哪一个包)–》包下的类的名字都有了一个别名(格式为:全部小写,或者是驼峰命名)
Mapper接口的映射配置文件(用于编写相关的SQL语句代码)
主要有四类标签:
insert标签:插入一条数据
update标签:修改一条数据
delete标签:删除一条数据
select标签:用于查询数据信息
select标签:在方法传参的时候方法的参数名在配置文件中通过占位符的形式进行拼接—》方法(int id)对应的配置为#{id}
属性:
(1)id:当前的SQL语句的唯一标识与Mapper接口中的方法名一致
(2)parameterType:指定方法传入参数的类型(可以不用指定)
(3)resultType:指定方法返回的类型
(4)resultMap:解决查询的时候字段名和Java实体类的属性名不一致的问题,多表查询也需要这个方法
public User findById(Integer id);<select id="findById" resultType="org.example.pojo.User">select id,user_name,birthday,sex,addressfrom userwhere id = #{id}
</select>
insert标签:接口方法传入的为一个对象的话,标签的value值为#{},#{},#{},#{}这些大括号中的值必须与对象的变量属性一样
<!-- 插入数据 --><insert id="addUser">insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address)values (#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})</insert>
#{value}: value值的参数与pojo中的实体对象的属性名一致
public class User {private Integer id;private String username;private Date birthday;private String sex;private String address;
}
update标签:
<update id="updateUser">update usersetusername=#{username},birthday=#{birthday},sex=#{sex},address=#{address}where id=#{id}
</update>
delete标签:
<delete id="deleteUser">delete from user where id=#{id}
</delete>
创建一个mybatis的工具类用于封装执行过程中的重复代码
(私有化构造方法,提供静态方法)
//创建一个工具类:私有化构造方法,提供静态方法
public class SqlSessionUtil {// 私有化构造方法private SqlSessionUtil(){}private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory=null;// 静态代码块,随着类的加载,只会执行一次static{//配置文件路径String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";//核心配置文件//基于配置文件路径,创建字节输入流对象InputStream is = null;try {is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);//创建SqlSessionFactory工厂类对象sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}// 提供静态方法,返回SqlSession对象public static SqlSession openSession(){// 返回SqlSession对象return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();// 默认为false,即不提交事务,不关闭连接}// 提供静态方法,返回SqlSession对象, 自动提交事务public static SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit){// 返回SqlSession对象return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(autoCommit);// true为自动提交事务,false为不提交事务,不关闭连接}// 提供静态方法,关闭SqlSession对象public static void close(SqlSession sqlSession){if(sqlSession!=null){sqlSession.close();}}
}
Mybatis中的两种占位符
${key}:在核心配置文件中获取外部配置文件中的数据
#{key}:配置映射文件XxxMapper.xml中的Sql占位符参数
两者使用的区别:
#{}:底层是使用PreparedStatement对象,对于Sql进行预编译,使用占位符的形式----》防止Sql注入
${}:底层是使用的Statement对象,对于Sql进行直接拼接----》会有SQL注入风险
多条件查询:
方式一:在接口方法中传入参数的时候通过@Param(“sql中参数的名字”)
(需要确保SQL映射文件中的SQL语句需要的参数名与这里的注解中的名字一样)
// 当方法传递的参数有2个以上的时,需要使用@Param("brandName")指定参数名,否则会报错
public List<Brand> findBrandByCondition(@Param("brandName") String brandName,@Param("companyName") String companyName,@Param("status") Integer status);
<select id="findBrandByCondition" resultMap="BrandMap">select id,brand_name,company_name,ordered,description,statusfrom tb_brandwherebrand_name = #{brandName}and company_name = #{companyName}and status = #{status}
</select>
方式二:通过实体类的行形式进行相关的查询
(需要确保SQL映射文件中的SQL语句需要的参数名与实体类的属性名一样)
//通过实体类的形式进行查询
public List<Brand> findBrandByCondition1(Brand brand);
<select id="findBrandByCondition1" resultType="com.example.pojo.Brand">select id,brand_name,company_name,ordered,description,statusfrom tb_brandwherebrand_name = #{brandName}and company_name = #{companyName}and status = #{status}
</select>
Brand.java
public class Brand {private Integer id;private String brandName;private String companyName;private Integer ordered;private String description;private Integer status;
}
方式三:通过map集合的形式进行传递多个参数
map.put()
@Test
public void testFindBrandByCondition2() {SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.openSession(true);BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);Map map = new HashMap();map.put("brandname", "华为");//这里的key和BrandMapper.xml中的SQL语句条件的参数名要一致map.put("companyname", "华为技术有限公司");map.put("status", 1);List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.findBrandByCondition2(map);for (Brand brand :brands) {System.out.println(brand);}
}
BrandMapper.xml中的参数为companyname对应的上面的测试方法中的map集合的key的名字
<select id="findBrandByCondition2" resultMap="BrandMap">select id,brand_name,company_name,ordered,description,statusfrom tb_brandwherebrand_name = #{brandname}and company_name = #{companyname}and status = #{status}
</select>
//通过Map集合的形式进行查询
public List<Brand> findBrandByCondition2(Map map);
针对于具体的实例来说用户可能在进行条件查询的时候可能不会将所有的参数都写上,可能会空着一些参数这时就需要用到**动态SQL**去解决具体的问题了
动态SQL
<if>标签:通过test的属性值设定判断条件(brandName这些参数名还是和传入的一致)
where 1=1
<if test="brandName != null">and brand_name = #{brandName}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null">and company_name = #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="status != null">and status = #{status}
</if>
<where>标签:代替where关键字,用于自动去除SQL语句中多余的and和or,同时不用写1=1这个条件了
例如:
select id, brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status from tb_brand WHERE brand_name = ?
<where><if test="brandName != null">and brand_name = #{brandName}</if><if test="companyName != null">and company_name = #{companyName}</if><if test="status != null">and status = #{status}</if>
</where>
**choose(when,otherwise)**标签相当于是Switch语句用法
<where><choose><when test="brandName != null">and brand_name = #{brandName}</when><when test="companyName != null">and company_name = #{companyName}</when><otherwise>and status = #{status}</otherwise></choose>
</where>
<set>标签:用于代替SQL语句中的set关键字,可以自动去除多余的逗号 ,
update tb_brand
<set><if test="brandName != null">brand_name = #{brandName},</if><if test="companyName != null">company_name = #{companyName},</if><if test="ordered != null">ordered = #{ordered},</if><if test="description != null">description = #{description},</if><if test="status != null">status = #{status},</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
批量删除(delete from 表名 where id in (1,2,3,4))换一种形式通过
标签<foreach>:用于遍历容器,获取容器中的元素,拼接SQL
<foreach collection=“用于遍历的集合/数组”
item=“从容器中取出的每一个元素”
separator=“元素之间的分隔符号”
open=“以‘xx’作为开始”
close=“以‘xx’作为结束”>
</foreach>
<delete id="deleteBrandById">delete from tb_brandwhere id in<foreach collection="ids"item="id"separator=","open="("close=")">#{id}</foreach></delete>














