【前言】
这章内容我会带着大家一步一步用PyTorch完成一个小项目。从构建数据集开始,一直到搭建模型、训练模型以及测试模型准确率。
【项目介绍】
给出一列电影评论,以及一列标签(标签内容为“neg”消极/“pos”积极),我们要做的是训练一个模型,根据评论判断出其是积极的还是消极的
一、导包
import pandas as pd import torch #用于加载数据集 from torch.utils.data import dataloader from torchvision import datasets# Dataset是抽象类,不能实例化,只能继承dataset类以后才能实例化 #用于制图 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
二、加载数据集
数据集来源:IMDB emotion analysis dataset
(1)pandas加载数据集
#加载训练集 xy=pd.read_csv(r"D:\学习\数据集\IMDB 情感分析数据集\train.csv")
(2)将label转换为数标签
#将评论文本标签转换为数值标签 xy["label"]=xy['label'].map({'pos':1,'neg':0})
(3)对review进行文本预处理
import pandas as pd import nltk from nltk.corpus import stopwords from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize import string# 定义文本预处理函数 def preprocess_text(text):# 转换为小写text = text.lower()# 去除标点符号text = text.translate(str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation))# 分词tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(text)# 去除停用词stop_words = set(nltk.corpus.stopwords.words('english'))tokens = [word for word in tokens if word not in stop_words]# 返回处理后的文本return text # 应用预处理函数 xy['text'] = xy['text'].apply(preprocess_text)
【注意】
1.要下载nltk包,安装过程非常麻烦,我将安装方法及过程放在下方,大家对照着教程来下载:【小沐学NLP】Python使用NLTK库的入门教程-CSDN博客
2.这串代码中preprocess_text(text)函数的text每一行的类型是字符串类型,这里着重记忆一下,后面会提到为什么一定要字符串类型。
(4)对review进行特征提取
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer# 使用 TF-IDF 转换文本数据 vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(max_features=5000) # 限制特征数量 X_tfidf = vectorizer.fit_transform(xy['text'])# 查看特征矩阵的形状 print("\nTF-IDF feature matrix shape:", X_tfidf.shape)
【强调】
X_tfidf = vectorizer.fit_transform(xy['text'])中fit_transform()函数的参数只能是字符串类型。
因此必须保证上一步处理得到的文本必须是字符串类型。
(5)将数据转换为PyTorch张量
# 将特征矩阵和标签转换为 PyTorch 张量 X_tensor = torch.from_numpy(X_tfidf.toarray()).float() # 将稀疏矩阵转换为 NumPy 数组,再转换为张量 y_tensor = torch.from_numpy(xy['label'].values).long() # 标签通常是整数型# 查看张量 print("\nX_tensor shape:", X_tensor.shape) print("y_tensor shape:", y_tensor.shape)
【使用PyTorch搭建模型】
三、搭建模型
import torch.nn.functional as Fclass LogisticRegression(torch.nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(LogisticRegression,self).__init__()#构建线性层self.linear1=torch.nn.Linear(5000,3000)self.linear2=torch.nn.Linear(3000,1500)self.linear3=torch.nn.Linear(1500,2)def forward(self,x):x=F.relu(self.linear1(x))x=F.relu(self.linear2(x))y_hat=F.sigmoid(self.linear3(x))return y_hat #实例化 model=LogisticRegression()
四、交叉熵损失函数、优化器
#损失函数 criterion=torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(size_average=True) #优化器 optimizer=torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.5)
五、训练模型
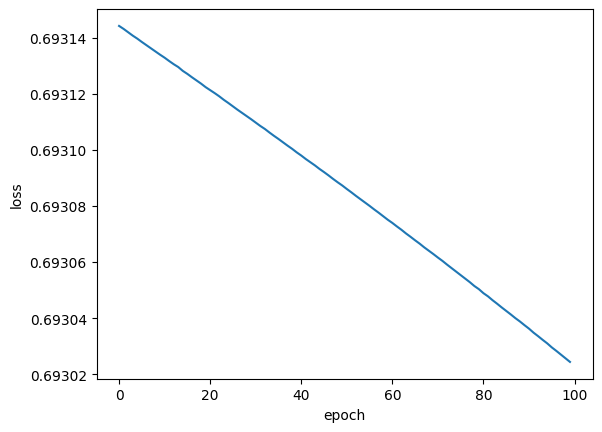
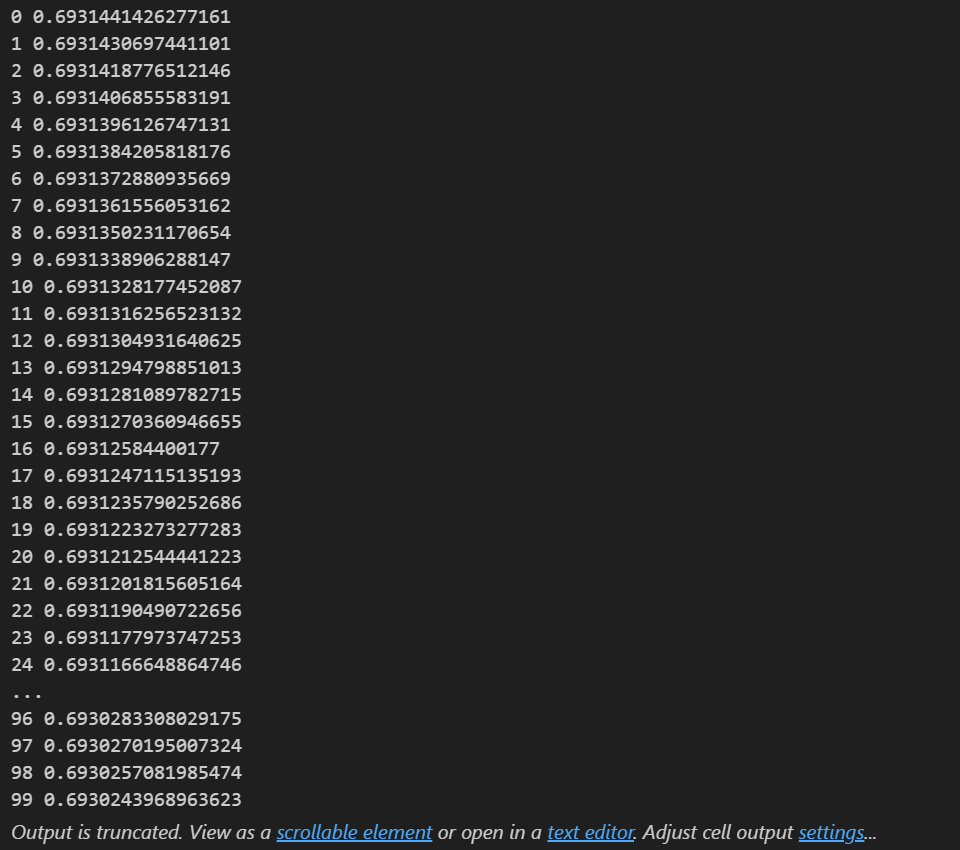
#训练模型 epoch_list=[] loss_list=[] for epoch in range(100):y_pred=model(X_tensor)loss=criterion(y_pred,y_tensor)print(epoch,loss.item())epoch_list.append(epoch)loss_list.append(loss.item())optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer.step()运行结果
构图
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.plot(epoch_list,loss_list)
plt.show()如图所示:
【使用Scikit learn机器学习中的模型直接进行训练,不用搭建内部框架】
三、训练模型
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score# 训练模型 model = LogisticRegression() model.fit(X_tensor, y_tensor)以下为运行结果
点击图中的“?”可以详细查看LogisticRegression()的详细使用教程
①LogisticRegression:用于创建逻辑回归模型。
②accuracy_score:用于评估模型的准确率
四、预测测试集
y_pred = model.predict(X_tensor)
model.predict 是 scikit-learn 中模型对象的一个方法,用于对输入数据进行预测。
具体来说:
①输入:X_tensor,一个二维数组(或类似结构),形状为 (n_samples, n_features),表示要预测的样本特征。
②输出:一个一维数组,形状为 (n_samples,),表示每个样本的预测类别标签。
对于二分类问题,model.predict 会输出每个样本属于正类(通常是类别 1)的概率,并根据设定的阈值(默认为 0.5)将样本划分为类别 0 或类别 1。
五、计算准确率
import create_data _,y_test=create_data.create_data(r"D:\学习\数据集\IMDB 情感分析数据集\test.csv")accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) print("Model accuracy:", accuracy)
使用 accuracy_score 计算模型的准确率,并打印结果
以下为create_data代码(其实就是把前面加载数据集的部分封装成了一个模块)
def create_data(file_path): """参数:数据集路径返回:元组(输入x,标签y)""""""一、导包"""import pandas as pdimport torchimport nltkfrom nltk.corpus import stopwordsfrom nltk.tokenize import word_tokenizeimport string"""二、加载数据集"""#(1)pandas加载数据xy=pd.read_csv(file_path)#(2)将评论文本标签转换为数值标签xy["label"]=xy['label'].map({'pos':1,'neg':0})#(3)对review进行文本预处理# 定义文本预处理函数def preprocess_text(text):# 转换为小写text = text.lower()# 去除标点符号text = text.translate(str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation))# 分词tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(text)# 去除停用词stop_words = set(nltk.corpus.stopwords.words('english'))tokens = [word for word in tokens if word not in stop_words]# 返回处理后的文本return text# 应用预处理函数xy['text'] = xy['text'].apply(preprocess_text)#(4)对review进行特征提取from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer# 使用 TF-IDF 转换文本数据vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(max_features=5000) # 限制特征数量X_tfidf = vectorizer.fit_transform(xy['text'])## 查看特征矩阵的形状#print("\nTF-IDF feature matrix shape:", X_tfidf.shape)#(5)将数据转换为PyTorch张量# 将特征矩阵和标签转换为 PyTorch 张量X_train_tensor = torch.from_numpy(X_tfidf.toarray()).float() # 将稀疏矩阵转换为 NumPy 数组,再转换为张量y_train_tensor = torch.from_numpy(xy['label'].values).long() # 标签通常是整数型## 查看张量#print("\nX_tensor shape:", X_train_tensor.shape)#print("y_tensor shape:", y_train_tensor.shape)return (X_train_tensor,y_train_tensor)if __name__=='__main__':x_train,y_train=create_data(r"D:\学习\数据集\IMDB 情感分析数据集\train.csv")print(x_train)print(y_train)












)


